How Do You Take The Birth Control Patch Off
On the same day of the following week, its time to remove the patch and apply a fresh one.
Simply peel it off and dispose by folding it in half so that it sticks to itself. Place in a sealed plastic bag and throw it away in the trash.
Apply a new patch using the above steps.
Do this for 3 weeks. On the fourth week, you can take a break from using the patch, starting again the week after. During this week, you may have a withdrawal bleed, which is similar to a period.
However, the Xulane patch can be applied during the fourth week to skip this bleed. You may still experience some bleeding or spotting for the first few months.
Article Content 3 Mins Read
- What is an Estrogen Patch?
- Benefits of an Estrogen Patch
- 1. Easy medication delivery
- 3. Avoiding the GI tract
- 4. Lower doses = lower risk
- 5. Reduces the risk of postmenopausal osteoporosis
- 6. May have a protective effect on the brain
Menopausal hormone therapy comes in various forms. Hormones can be delivered to your body via the vaginal route or in the form of a pill, cream, or patch.
What Are The Disadvantages Of The Birth Control Patch
There are a number of factors to keep in mind when it comes to choosing the patch. Talk to your healthcare provider about any previous or current conditions you have, including breast cancer, diabetes, migraine, if you think you might be pregnant, and what drugs and supplements youre currently taking. Because of the way the patch works, youll actually be exposed to 60% more estrogen than if you were taking an oral contraceptive with the same level of estrogen. If youre sensitive to estrogen or currently have or have had a medical history of estrogen-related conditions, including breast cancer, this would be something to take into serious consideration. Smokers over 35 are advised against using the patch. Additionally, there are a few other downsides to Xulane:
- The patch doesnt protect against STIs, so youll need to use condoms if thats a concern.
- Drug interactions may make the patch less effective.
- Its less effective if youre unable to change the patch on time or if it gets loose regularly.
- Its less effective if you weigh over 198 pounds.
- Skin irritation and rashes may occur at the patch site.
- There are more serious risks, such as blood clots, heart attack, high blood pressure, gallbladder disease, liver cancer, and stroke
- Timing restrictions require the patch be changed on the same day every week.
Recommended Reading: Best Pill To Balance Hormones
The Patch And Depression
A 2016 study by scientists in Denmark found that women who used hormonal birth control were more likely to be prescribed antidepressants compared to women who were not on birth control. Women who were on the Patch were the most likely to take antidepressants compared to women on all of the different forms of birth control that were studied. Teenagers who were on the Patch were the most likely to be treated for depression. While this study does not prove that the Patch causes depression, that is a logical explanation.
What Happens If I Don’t Have A Withdrawal Bleed Between Patches

Sometimes not all women have a bleed during their patch-free week. If you have used your contraceptive patch properly, if it has not fallen off and if you have not taken any medication that may interfere with the patch, you are unlikely to be pregnant. If you are worried, you can do a pregnancy test or you can visit your GP, practice nurse, family planning clinic or sexual health clinic for advice. If you miss two periods, you should seek medical advice.
Recommended Reading: How To Increase Your Testosterone Naturally
What Side Effects Should I Expect From The Birth Control Patch
The hormones in the birth control patch may cause side effects in some people. But this doesnt happen to everyone many people use the patch with no problems.
After starting the patch, some people may have:
-
Changes in your periods
-
Skin reactions where the patch goes
The good news is that these side effects usually go away in 2-3 months. So if you just started using the patch and you have side effects that bother you, try to stick it out and give your body a chance to adjust to the hormones.
Birth control shouldnt make you feel sick or uncomfortable. If you still dont like the way the patch makes you feel after a few months, talk with your nurse or doctor. They may suggest a different birth control method. Some people try a few different types of birth control before finding the right one for them.
And remember: if you stop using the patch and dont use another birth control method, youll be at risk for pregnancy right away.
The hormones in the patch and other types of birth control have been around for decades, and millions of people have used them safely. Side effects of the patch arent dangerous . You can always call a nurse or doctor, like the staff at your local Planned Parenthood health center, if you have any concerns while using the patch. And you can keep track of any potential side effects with our birth control app.
Is The Menopause Patch Safe
Yes, both the pill and the patch have been shown to be safe and effective treatments for the symptoms of menopause. But when comparing the two, one study that followed 54,000 women for one year found that those who used estrogen patches were one-third less likely to develop blood clots in their legs or lungs.
Though there are some unique benefits of the estrogen patch, the science is clear: hormone therapy is safe and effective at providing relief from menopause symptoms, regardless of the form of delivery.
Read Also: Hormone Therapy For Erectile Dysfunction
What Are The Side Effects Of The Birth Control Patch
Some women have skin irritation when they use the contraceptive patch. This is usually itching, redness or soreness. About 2 in 100 women have to stop using the patch because of skin irritation. Even though the patch sticks well most of the time, there is a possibility that it can become detached from the skin, either totally or partially. This is not common but can mean that its effectiveness as contraception can be lost. Despite its discreet design, some women still feel that the contraceptive patch can be seen.
Some women have some other mild side-effects when they first start using the contraceptive patch. If side-effects do occur, they tend to settle down within the first few months. Possible side-effects can include:
- Breast discomfort and tenderness.
- Slight changes in body weight. These weight changes are small and are similar to those that can occur with the COC pill. Studies have shown the patch does not cause significant weight gain.
- Bleeding between your periods, and spotting .
How Does The Contraceptive Patch Work
The contraceptive patch works mainly by changing the body’s hormonal balance so that you do not produce an egg every month . It also makes the cervical mucus thicker, forming a plug in the neck of the womb . This makes it difficult for sperm to get through to the womb to fertilise an egg. The hormones in the contraceptive patch also make the lining of the womb thinner, so it is less likely that a fertilised egg will be able to attach to the womb.
Read Also: Can Imbalanced Hormones Cause Anxiety
How Well Does It Work
In the first year of use:
- When the patch is used exactly as directed, fewer than 1 person out of 100 has an unplanned pregnancy.
- When the patch is not used exactly as directed, 9 people out of 100 have an unplanned pregnancy.
Be sure to tell your doctor about any health problems you have or medicines you take. Your doctor can help you choose the birth control method that is right for you.
What Do I Do When I Want To Stop Using The Patch
This depends on your plan for contraception after the patch. If you do not need contraception any more, either because you plan to have a baby or because you are not in a relationship, you can just stop it any time. Ideally stop it at the end of week 3 when you would normally come to the end of the cycle. If you do this, it will cause less disruption to your monthly bleeding cycle. However, if you wish to take the patch off before the end of the cycle, you may do so any time as long as you have not had unprotected sex in the previous five days.
If you still need contraception then speak with your doctor or nurse about how to swap to a different type of contraception in a way which will provide continuous protection as you swap over.
Recommended Reading: What Birth Control Is Best For Hormonal Imbalance
How Do I Put My Patch On
You can apply the patch like you would a Band-Aid. You must apply a new patch each week. Be sure that the spot where you have decided to wear your patch is clean and dry. Do not place the patch over irritated skin such as a rash or cut. Lotions on this area will cause the patch not to stick.
- With clean dry hands, open the foil package and remove the patch.
- Remove the clear plastic that covers the patch.
- While holding the nonstick side, firmly press the patch on your skin for about 10 seconds.
- Check the edges of the patch to be sure that it is stuck firmly to your skin.
- Throw the clear plastic cover away.
Does The Birth Control Patch Have Good Side Effects
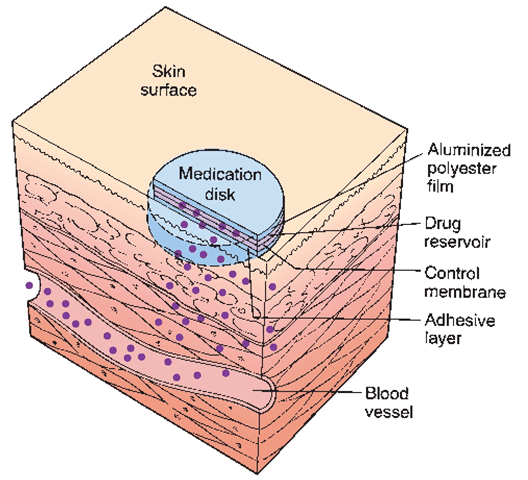
Side effects arent always a bad thing many people use the patch because some of the side effects can be really helpful. For example, the hormones in the patch can help with painful, heavy, or irregular periods. The patch may ease cramps and PMS, and it will usually make your periods lighter and more regular. You can even use the patch to safely skip your period.
The changes in your periods while on the patch can sometimes make people worry about being pregnant. But the chance of pregnancy is very low as long as youre using the patch correctly. If youre worried, you can always take a pregnancy test to be sure.
The birth control patch can also help prevent acne, iron deficiency , bone thinning, cysts in your breasts and ovaries, and certain cancers.
Read Also: How Does Melatonin Make You Sleep
Are There Any Risks Or Side Effects To Keep In Mind
The estrogen patch isnât right for everyone. Women with certain medical conditions or predispositions will need to be assessed closely by a medical provider to determine their eligibility for HT, and type of HT. These risk factors are highly personalized and vary depending on a womanâs age, and her individual medical history.
A personal history of the following conditions could put you at risk for vascular complications on HT:
- Breast or uterine cancer
- Certain heart or vascular conditionsâsuch as blood clots, stroke, heart attack, coronary heart disease, or uncontrolled hypertension.
- Unexplained vaginal bleeding
Screening for these risk factors is a standard part of the assessment for HT eligibility and treatment, including treatment with Evernow.
If youâre interested in finding out whether you are a good candidate for hormone replacement therapy with Evernow, .
How Effective Is It
According to Planned Parenthood, the failure rate is less than 1 percent for women who always use the patch according to the directions. Its about 9 percent for women who dont always use the patch according to the directions.
To help increase effectiveness, change your patch at the same time on the same day each week. Decide which day and time would be easiest for you before you start using the patch.
You May Like: How Can You Balance Your Hormones Naturally
Do Other Medicines Interfere With The Contraceptive Patch
Some medicines can interfere with it and make it less effective. You should always discuss all other medication that you are taking with the person prescribing the patch. This includes over-the-counter medications which may also interfere with the contraceptive patch. If you are starting a new medication, make sure that you tell the person prescribing it that you are using the contraceptive patch. You may need to use extra contraceptive precautions while you are taking the other medication and for a period of time after it is finished.
Some commonly encountered medicines that can interfere with the contraceptive patch include certain antibiotics , some medicines used to treat epilepsy , some medicines used for HIV infection, and, as mentioned above, St John’s wort .
Note: antibiotics which are commonly used do not interfere with the effectiveness of the contraceptive patch.
How Do You Put The Birth Control Patch On
First, decide where you want to apply the patch. This should be an area of clean, dry skin, such as your:
Here are places you should avoid placing the patch:
- any areas that are sore or irritated
- areas that might get rubbed with tight clothing
- areas where you might apply lotion, powder, or makeup to help keep the patch sticky
Open the foil pouch so that it lies flat and peel the patch off the foil.
Next, peel half of the plastic off the patch. Be careful not to touch the sticky part.
Stick the patch to your skin, peeling off the rest of the plastic. Push it against the skin for 10 seconds using the palm of your hand.
You May Like: Does Low Testosterone Affect Sperm Count
How Do You Use The Birth Control Patch
The patch is a prescription and must be obtained from your healthcare provider. The patch is worn for one week at a time and it is placed directly on the skin of your buttocks, stomach, upper arm or upper torso.
The patch is replaced once a week on the same day each week for three weeks in a row. The patch is not worn during the fourth week to allow your menstrual flow to occur at this time.
Can I Avoid The Withdrawal Bleed
Occasionally, for special occasions such as holidays or exams, you can choose to miss your monthly withdrawal bleed . To do this, do not have a patch-free week. When you get to the end of week 3, simply put on another patch and start the cycle as if it is week 1. This will not always work, and you may have some breakthrough bleeding. If you have used the patch correctly every seven days, you are unlikely to be pregnant. If you prefer not to have a period or withdrawal bleed at all, you could consider other methods of contraception instead of the contraceptive patch. There are some contraceptive options where periods are extremely light or do not occur at all. These include the contraceptive implant, the intrauterine system, and contraceptive injections.
Don’t Miss: How Do You Know If Your Estrogen Levels Are Low
If You’re Under 16 Years Old
Contraception services are free and confidential, including for people under the age of 16.
If you’re under 16 and want contraception, the doctor, nurse or pharmacist won’t tell your parents , as long as they believe you fully understand the information you’re given and the decisions you’re making.
Doctors and nurses work under strict guidelines when dealing with people under 16. They’ll encourage you to consider telling your parents, but they won’t make you.
The only time that a professional might want to tell someone else is if they believe you’re at risk of harm, such as abuse. The risk would need to be serious, and they would usually discuss this with you first.
Page last reviewed: 6 July 2021 Next review due: 6 July 2024
Are There Any Problems With The Birth Control Patch

The birth control patch is a safe and effective method of birth control. Most people who use the patch have no side effects. Smoking cigarettes while using the patch can increase the risk of certain side effects, which is why health professionals advise those who use the patch not to smoke.
Side effects that can happen with the patch are similar to those with the birth control pill. These may include:
- irregular menstrual bleeding
You May Like: What Is Melatonin For Dogs
Uses Of Birth Control Patches
Birth control patches are a type of hormonal contraception, like the pill or the ring. They deliver a combination of estrogen and progestin through the skin.
Unlike birth control pills, also known as oral contraceptives, you only need to stick on a patch once a week. You will wear each patch for a week at a time and then, after three weeks, take a week off to allow a withdrawal bleed.
Birth control patches work by stopping ovulation. When the body does not produce an egg, there is no way to become pregnant.
When used perfectly, hormonal contraception is highly effective. But many people miss doses or otherwise have problems that make their contraceptives less effective. This may be particularly true for adolescents. No birth control method apart from abstinence is 100% effective in preventing pregnancy.
In general, people are more likely to use a birth control patch correctly than a birth control pill. However, people who use the patch may be more likely to stop using it because of side effects.
Recommended Reading: Does Blue Cross Blue Shield Cover Testosterone Therapy
Hormones And Oral Contraceptive Use
Most of the data that attributed a risk of stroke to the use of oral contraceptives were acquired in patients who used pills with a relatively high estrogen content .183185,185a In these studies, hypertension, migraine, diabetes, hyperlipidemia, cigarette smoking, age older than 35 years, and prolonged use of oral contraceptive pills compounded the risk of ischemic stroke in oral contraceptive users. Lower-dose estrogen combined with newer progestational drugs are now usually prescribed as oral contraceptive agents. Studies show that young women who take these lower-dose pills do not have an important increased risk of stroke.186189 Contraceptive patches that contain 35 g of ethinyl estradiol did not increase the risk of ischemic stroke or myocardial infarction in one study.190 Among users of low-dose contraceptives, strokes most often occur in older women who have other stroke risk factors, such as hypertension and cigarette smoking.191 Genetics also probably play a role, but this has been inadequately explored. Patients with prothrombin gene mutations have an increased risk of stroke when they take oral contraceptives.192 The presence of factor V Leiden prothrombin gene mutations other causes of resistance to activated protein C abnormalities of antithrombin III, protein C, and protein S and other genetic-related disorders of coagulation proteins might make women who take oral contraceptives or smoke cigarettes especially susceptible to thrombosis.
You May Like: How To Get Your Hormones Back In Balance Naturally