Less Common Types Of Hormone Therapy
Some other types of hormone therapy that were used more often in the past, but are rarely given now include:
- Megestrol acetate , a progesterone-like drug
- Androgens , like testosterone
These might be options if other forms of hormone therapy are no longer working, but they can often cause side effects.
B Bone Modifying Therapies
As estrogen plays an important role in bone homeostasis, systemic therapies that potentially decrease levels of estrogen can also reduce bone mineral density . In breast cancer, the potential risk of BMD loss is affected both by patient age and by therapy received . Patients receiving AIs or GnRH agonists may have increased short and long term osteoporotic fracture risks. In these patients, BMD testing at least every 2 years is recommended, in addition to dietary supplementation of calcium and vitamin D, exercise and lifestyle modifications such as smoking cessation .
In addition to the effects on BMD, bisphosphonates have been shown to have anti-cancer therapeutic effects and are associated with improved breast cancer survival in post-menopausal women. An EBCTCG meta-analysis demonstrated that among post-menopausal women, the use of bisphosphonates reduced bone fractures, breast cancer recurrence, breast cancer recurrence in bone, distant metastases and breast cancer related deaths, irrespective of HR status, tumor grade, nodal involvement or chemotherapy use .
The Following Statistics Are A Little Old Now They Are Much Better
There are of course many factors that contribute to the survival of breast cancer. However, some older studies show that only about 60%of patients with HER-2 positive status invasive breast cancer are disease free after 10 years.
In addition, about 65% survive overall .
And, a greater number of HER-2 positive patients succumb to the illness during the first five years than those who are negative for HER-2 overexpression.
At the same time, all other factors assumed to be equal, patients with negative HER-2 status tumors tend to be disease free at a rate of 75% over 10 years and have a slightly higher overall survival rate.
From this, we can informally estimate that women with breast cancer which overexpresses HER-2 are about 10% more likely to have significant difficulties and ultimately succumb to the disease within the first five years, than those who do not.
Because some of the Incidence and Prognosis rates are a little old now check out our brand new Index of Posts on Survival Rates.
You May Like: Breast Cancer Weight Gain Symptom
Read Also: Hormonal Therapy For Prostate Cancer Side Effects
Conflict Of Interest Disclosures
We have read and understood Current Oncologys policy on disclosing conflicts of interest, and we declare the following interests: AAJ has previously provided advisory board services to Roche, Novartis, Pfizer, Eisai, and AstraZeneca, and has received educational meeting travel support from Novartis and AstraZeneca . MG and RF have no conflicts to declare. MJC has previously received meeting support from Amgen and Novartis, and has received educational meeting travel support from Novartis .
Donât Miss: Life Expectancy Of Breast Cancer Survivors
Finding The Type Of Cancer
A pathologist looks at the cancer cells under a microscope to see which type of breast cancer it is. They can tell this by the shape of the cells and the pattern of the cells in the breast tissue.
Pathologists also sometimes use particular dyes to stain the cells and show up certain proteins or features of the cells.
Recommended Reading: The Hormone Reset Diet Recipes
Estrogen And Progesterone Receptor Agonists
Several alternative hormone therapies have been utilized with variable success over the last decades and remain as options to be considered with the goal of delaying chemotherapy for advanced disease as long as possible. Megestrol acetate and estradiol represent cheaper options that need to be taken into consideration. Many women may be on long-term treatment on drugs not always fully covered by insurance and in LMIC, novel therapies are unavailable due to their high price.
Progestins have a reported ORR of 25% but are associated with side effects such as weight gain, fluid retention and an increase in the risk of thromboembolic events . Medium and high dose estradiol or diethylstilbestrol have been paradoxically used in the treatment HR+ MBC with similar response rates compared to tamoxifen but a higher toxicity profile . Estradiol may be administered at 6 mg daily, which was shown to be as effective and much less toxic than the previously recommended 30 mg daily dose . Bisphosphonates must be co-administered to avoid hypercalcemia and medroxyprogesterone acetate should be given for the last 5 days of the month to avoid dysfunctional uterine bleeding. Ideal patients for estradiol therapy are those that have experienced long term disease control with an AI before disease progression.
How Does Hormone Therapy Work
About 2 out of 3 breast cancers are hormone receptor-positive. Their cells have receptors for estrogen and/or progesterone which help the cancer cells grow and spread.
There are several types of hormone therapy for breast cancer. Most types of hormone therapy either lower estrogen levels in the body or stop estrogen from helping breast cancer cells grow.
Also Check: Can Hormones Cause Weight Gain
Dna Damage Response Inhibitors
DNA damage response detecting and repairing damaged genes through a variety of ways is a vital protective mechanism to maintain genome stability and prevent breast cancer. DNA single-strand break is mainly repaired by three ways: base excision repair , nucleotide excision repair , and mismatch-repair , and the more serious DNA double-strand break is repaired through two additional pathways: homogeneous recombination and non-homologous end joining .
HR is an error-free repair process, depending on the availability of homologous DNA templates and mainly playing a role in the G2/M phase of the cell cycle. Although NHEJ is more error-prone compared to HR, it is considered to be the main way of DSB repair and works in all phases of the cell cycle .
Mutations in the DDR gene occur in all kinds of breast cancer. Deletion or mutation of BRCA1/2 is present in 10% of patients . DNA dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit , a member of the phosphatidyl inositol-3-kinase-like kinase family that is involved in NHEJ and maintains the structural stability of telomeres, is down-regulated in 57% of early breast cancer cases . In TNBC, BRCA, nonâBRCA HR, and nonâHR DDR genes have mutations , and quite a few proteins involved in DDR including PARP-1 are overexpressed .
A large number of studies have represented that DDR targeted drugs have the potential to treat breast cancer. As shown in Figure 2, an overview of the DNA damage response and repair pathways is detailed below.
Et Combinations With Targeted Therapies
Over the last decade, targeted therapies that modulate mechanisms of ET resistance have been incorporated into clinical practice. Two general patterns of ET resistance are recognized clinically: intrinsic resistance, referring to cases where ER+ cancers never adequately respond to ET and acquired resistance, which occurs after an initial response to endocrine manipulation . These definitions are not precise and the underlying mechanisms between intrinsic and acquired resistance are likely to overlap. Several cell-autonomous and non-cell-autonomous alterations in ER+ breast cancer and a variety of components of the interaction of breast cancer cells with the tumor microenvironment could lead to mechanisms of resistance to ET. These mechanisms are described in Figure 1 and include deregulation of the ER pathway, the cell-cycle machinery, growth factor receptor signaling, secondary messengers, apoptosis and senescence, epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition , cancer stem cell persistence, and signaling within the tumor microenvironment. Comprehensive reviews regarding mechanisms of ET resistance have been published elsewhere and are beyond the scope of this article . We do not discuss the subgroup of ER+ HER2 positive patients in detail here but do point out there are a number of phase 2 and phase 3 trials that indicate that the combination of HER2 targeting with ET produced prolonged responses in some patients .
Figure 1
Also Check: Does Melatonin Cause Night Sweats
Antiangiogenic Effects Of Other Drugs
Endocrine therapy for breast cancer is mostly used in ER positive patients, and tamoxifen is the most commonly used anti-estrogen therapy. Existing data indicate that a variety of estrogen hormones, such as estradiol and progesterone, increase the expression level of VEGF in breast cancer , while tamoxifen can inhibit the secretion of VEGF and reduce the density of vascular endothelial cells in breast cancer by more than 50%, the mechanism of which is related to the regulation of the expression ratio of VEGF and sVEGFR-1 .
In addition, there is a crossover between the downstream signaling pathway of ER and VEGF signaling pathway in breast cancer , which provides a theoretical basis for clinical endocrine therapy combined with other angiogenesis inhibitors.
When Is Hormone Therapy Used For Breast Cancer
Hormone therapy is often used after surgery to help reduce the risk of the cancer coming back. Sometimes it is started before surgery .
It is usually taken for at least 5 years. Treatment longer than 5 years might be offered to women whose cancers have a higher chance of coming back. A test called the Breast Cancer Index might be used to help decide if a woman will benefit from more than 5 years of hormone therapy.
Hormone therapy can also be used to treat cancer that has come back after treatment or that has spread to other parts of the body.
Also Check: How Can I Boost Testosterone
What This Means For You
If youve been diagnosed with advanced-stage, hormone receptor-positive, HER2-negative breast cancer and are deciding on first treatments with your doctor, the results of this study may be promising.
But its important to remember that dalpiciclib is not approved to be used in the United States unless its being used in a clinical trial.
And its also important to know there are three other CDK4/6 inhibitors that are available in the United States, so you have treatment options.
Still, some of the CDK4/6 inhibitors available in the United States may not be as readily available in certain parts of China.
The progression-free survival results suggest extension of dalpiciclib approval to the first-line metastatic breast cancer setting in the Chinese population, Meritxell Bellet, MD, PhD, medical oncologist at the Vall dHebron Institute of Oncology in Barcelona, Spain, said in her discussion of the results.
Learn more about CDK4/6 inhibitors.
What Is Hormone Therapy
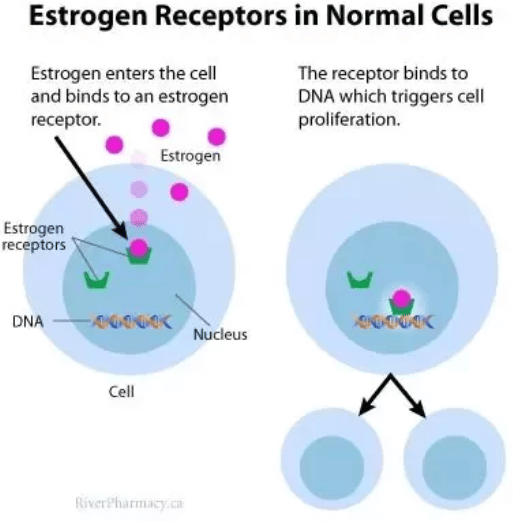
Hormone therapy slows or stops the growth of hormone-sensitive tumors by blocking the bodys ability to produce hormones or by interfering with effects of hormones on breast cancer cells. Tumors that are hormone insensitive do not have hormone receptors and do not respond to hormone therapy.
Hormone therapy for breast cancer should not be confused with menopausal hormone therapy treatment with estrogen alone or in combination with progesterone to help relieve symptoms of menopause. These two types of therapy produce opposite effects: hormone therapy for breast cancer blocks the growth of HR-positive breast cancer, whereas MHT can stimulate the growth of HR-positive breast cancer. For this reason, when a woman taking MHT is diagnosed with HR-positive breast cancer she is usually asked to stop that therapy.
Also Check: What’s The Best Amount Of Melatonin To Take
Advances In Chemotherapy For Her2
Hirofumi Mukai, Mayuko Ito
Department of Breast and Medical Oncology, National Cancer Center Hospital East , , Japan
Contributions: Conception and design: H Mukai Administrative support: H Mukai Provision of study materials or patients: H Mukai Collection and assembly of data: H Mukai Data analysis and interpretation: H Mukai Manuscript writing: All authors Final approval of manuscript: All authors.
Correspondence to:
Abstract: Metastatic breast cancer cannot be curable, but significant improvement in overall survival has been observed with the appearance of new agents. The purpose of treatment is to prolong survival and to improve quality of life by reducing cancer-related symptoms. To achieve these goals, individualized approach is required. Chemotherapy is used for patients with hormone receptor negative breast cancer or hormone receptor positive patients who have cancer-related symptoms. The choice of regimen , selection of a specific therapy and the duration of treatment depend on multiple factors, including the tumor burden, general health status, prior treatments and toxicities, and patient preferences.
Keywords: Breast cancer chemotherapy quality of life survival
Submitted Apr 02, 2018. Accepted for publication May 31, 2018.
doi: 10.21037/cco.2018.06.01
What Are The Side Effects Of Hormone Therapy
The side effects of hormone therapy depend largely on the specific drug or the type of treatment . The benefits and harms of taking hormone therapy should be carefully weighed for each person. A common switching strategy used for adjuvant therapy, in which patients take tamoxifen for 2 or 3 years, followed by an aromatase inhibitor for 2 or 3 years, may yield the best balance of benefits and harms of these two types of hormone therapy .
Hot flashes, night sweats, and vaginal dryness are common side effects of all hormone therapies. Hormone therapy also may disrupt the menstrual cycle in premenopausal women.
Less common but serious side effects of hormone therapy drugs are listed below.
Tamoxifen
- breathing problems, including painful breathing, shortness of breath, and cough
- loss of appetite
Also Check: Hormone Pellets And Breast Cancer
Hormone Receptor Status And Hormone Therapy
Hormone receptor-positive breast cancers can be treated with hormone therapies.
Hormone therapy drugs include tamoxifen and the aromatase inhibitors, anastrozole , letrozole and exemestane . Ovarian suppression, with surgery or drug therapy, is also a hormone therapy.
Hormone receptor-negative breast cancers are not treated with hormone therapies because they dont have hormone receptors.
Also Check: Hormonal Breast Cancer Symptoms
If Cancer Comes Back Or Has Spread
AIs, tamoxifen, and fulvestrant can be used to treat more advanced hormone-positive breast cancers, especially in post-menopausal women. They are often continued for as long as they are helpful. Pre-menopausal women might be offered tamoxifen alone or an AI in combination with an LHRH agonist for advanced disease.
Also Check: Can Melatonin Cause Memory Loss
Choice Of Adjuvant Endocrine Therapy In Post
Suggested Adjuvant Endocrine Therapy Approach for Women who are Post-Menopausal at Diagnosis
AI: Aromatase Inhibitor ET: Endocrine Therapy
*High risk disease defined as tumors with lymph node involvement or aggressive histological features. In lymph node negative disease, high risk defined as large tumor size or poor prognosis identified by genomic assays
^ Extended tamoxifen may be appropriate in post-menopausal patients if toxicities or contraindications to AI
Several adjuvant endocrine therapy options are available for post-menopausal women including AI for 5 years, tamoxifen for 5 years , tamoxifen for 2-3 years followed by AI to complete 5 years, tamoxifen for 2-3 years followed by 5 years of AI, tamoxifen for 5 years followed by AI for 5 years. While patient factors and patient preferences should be considered, most guidelines recommend the use of an AI, either for 5 years, or for 2-3 years after prior tamoxifen use if possible . Extended AI therapy may be considered for select women and is discussed below.
B Ovarian Function Suppression With Tamoxifen Or An Aromatase Inhibitor
OFS by surgical or pharmacological means should be considered in high-risk pre-menopausal patients. Surgical OFS via bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy is irreversible and may be a suitable option for women with increased risk of ovarian cancer, and in those who desire permanent OFS. Pharmacological methods are generally reversible and use gonadtropin-releasing hormone agonists such as goserelin and leuprolide to suppress luteinizing hormone and follicle-stimulating hormone and subsequently reducing estrogen production from the ovaries . While initial studies of OFS versus no adjuvant therapy and OFS versus adjuvant chemotherapy failed to demonstrate a reduction in recurrence or death overall , data have suggested that OFS benefits may be observed in younger, pre-menopausal women .
Read Also: How To Tell If Hormones Are Out Of Whack
Understanding Hormone Receptor Test Results
Most labs use a special staining process that makes hormone receptors show up in a sample of breast cancer tissue. The test is called an immunohistochemical staining assay, or ImmunoHistoChemistry . Not all labs use the same method for analyzing the results of the test, and they don’t report the results in exactly the same way. So you may see any of the following on your pathology report:
- Advertisement
A percentage that tells you how many cells out of 100 stain positive for hormone receptors. You will see a number between 0% and 100% .
- Advertisement
An Allred score between 0 and 8. This scoring system is named for the doctor who developed it. The system looks at what percentage of cells test positive for hormone receptors, along with how well the receptors show up after staining, called intensity. This information is then combined to score the sample on a scale from 0 to 8. The higher the score, the more receptors were found and the easier they were to see in the sample.
- Advertisement
The word positive or negative.
Keep in mind that the breast cancer should be tested for both estrogen receptors and progesterone receptors. If your result is reported as just positive or negative, ask your doctor for a more definite percentage, rating, or other number. You also can ask about how these more precise results might influence treatment decisions for your particular situation.
Most breast cancers are hormone receptor positive:
Learn more at Hormonal Therapy.
All About Er Positive Her2 Negative Breast Cancer
About one in eight women in the United States will develop breast cancer, according to commonly used statistics.
But other reports indicate that breast cancer rates are on the decline, likely because of improved recognition, prevention, and treatment. One advancement is the ability to identify different breast cancer types based on specific molecules found in tumors. The distinction greatly aids in breast cancer treatment selection and helps doctors predict how aggressive cancers will advance.
A crucial step in the process of beast cancer evaluation is testing tumor tissue removed during a biopsy or surgery to determine if it has estrogen and progesterone receptors molecules that the hormones bind to.
Cancerous cells may have none, one, or both receptors. Breast cancers that have estrogen receptors are called ER-positive . Those with progesterone receptors are referred to as PR-positive .
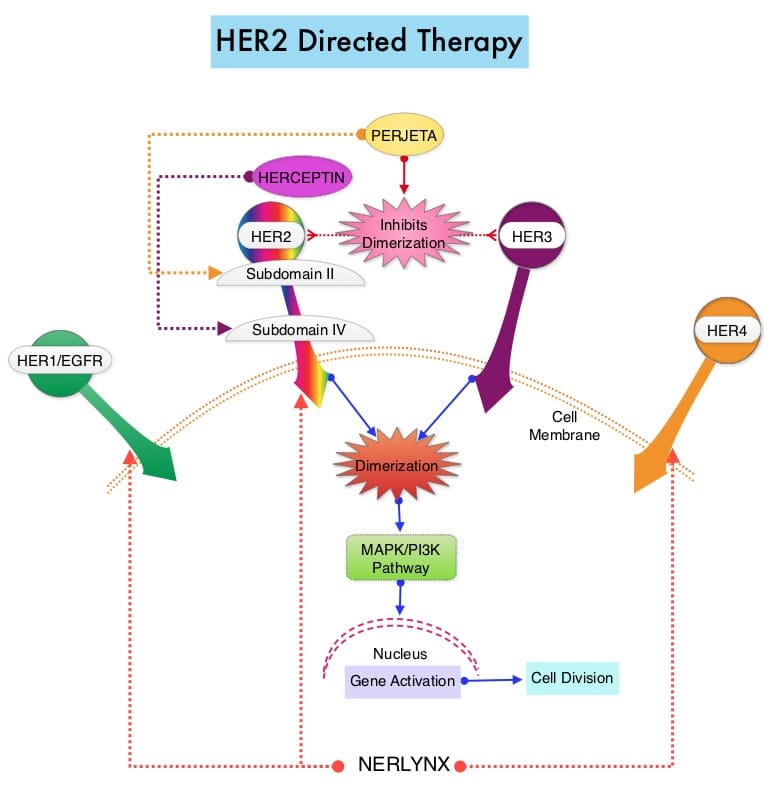
In addition to hormone receptors, some breast cancers have high levels of a growth-promoting protein called HER2/neu. If a tumor has this property, it is called HER2-positive. HER2 positive cancers are more aggressive than HER2 negative cancer.
Knowing breast cancer type, leads doctors to determining best treatments.
HER2 negative cancers will not respond to treatment with drugs that target HER2, such as trastuzumab and lapatinib .
Overall, estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer is treatable, especially when diagnosed early.
Don’t Miss: Can You Of On Melatonin