Do You Have Low Progesterone Or High Estrogen
Last updated on By Jing
Low progesterone and high estrogen can both manifest as PMS, period pain, or other menstrual disharmonies. So how can you tell which is the cause of your symptoms?
If you suffer from PMS, period pain, or other menstrual disharmonies, you may be wondering if they are caused by high estrogen or low progesterone.
Youve probably learned that high estrogen levels can produce PMS, mood swings, fibroids, PCOS, endometriosis, and a whole slew of other menstrual problems.
But so can progesterone deficiency, because estrogen dominance is often accompanied by low progesterone levels .
It can be confusing to sort through the often-contradictory symptoms and come up with a correct diagnosis.
Physical And Mental Symptoms Of High Estrogen Versus Low Progesterone
Estrogen dominance tends to manifest itself as various symptoms of excess, such as bloating, nausea, gas, acne, breast tenderness, pulsing headaches, etc.
Whereas progesterone deficiency can make you feel tired, or cause you to experience a mental fog, food cravings, diarrhea, dizziness, dull headaches, or a decreased sexual desire.
Both high estrogen and low progesterone can cause insomnia. To learn the difference, check out high estrogen insomnia versus low progesterone insomnia.
Menstrual Symptoms Of High Estrogen Versus Low Progesterone
When estrogen levels are too high, there may be a build-up of the uterine lining, which can cause intense, stabbing pains during period, and heavy menstrual bleeding with dark clots.
Due to the stagnation in the reproductive organs, you may feel bloated in the abdomen, have swollen and painful breasts, or experience pain one to two days before your period.
Since progesterone deficiency often accompanies estrogen dominance, you may experience similar symptoms if your progesterone levels are low. But the strength is likely to be weaker.
For example, you may have more of a dull pain or dragging sensation in the lower abdomen, which is often relieved by pressure or massage. The color of your menstrual blood is not as dark, and the amount of your bleeding is also less.
As you can see, though similar, the signs of estrogen dominance versus symptoms of progesterone deficiency differ in intensity and strength.
Here are a couple simple questions to ask yourself when faced with mixed signs: Do my overall symptoms suggest excess or deficiency? Do I feel robust or weak?
If you feel weak and have more of the symptoms of deficiency, you might want to focus on supporting progesterone. Review the 7 common causes of progesterone deficiency and learn how to use natural supplements to increase your progesterone production naturally.
I hope you find this post helpful. As always, please leave a comment to share your questions, thoughts and experiences.
Read Also: Cost Of Estradiol Without Insurance
Youre Feeling Down Or Depressed
Estrogen helps your body produce serotonin, which is a neurotransmitter that helps boost your mood. If you have low estrogen, your serotonin is likely lower, too.
“Low estrogen can affect your mood by influencing neurochemical pathways linked to depression” says Dr. Eyvazzadeh. “Animal and human studies have shown how estrogen and progesterone affects brain regions involved in mood. Both estrogen and progesterone influence known regions in the brain.”
Estrogenâs connection to serotonin also explains why you might be experiencing depression. Estrogen boosts serotonin, which helps your body combat depression. So if you have low estrogen, your low serotonin levels canât stave off sad feelings.
How Doctors Treat Hormonal Imbalances

There isnt one best medication for low estrogen. What works for you will depend on a few different factorsincluding the underlying cause of your hormonal imbalances, if other hormones are affected, and your specific personal and family medical history. Your doctor may ask you to come back a few times to test your blood and fine-tune your treatment.
Dr. Ayazo explains that your physician will look at all of these different factors to find a treatment that works best for you. Some possible options include:
Don’t Miss: Blue Cross Blue Shield Testosterone Coverage
How Often Do I Need To See My Doctor After Menopause
You should still see your healthcare provider for routine gynecological care even though you aren’t menstruating. This includes Pap tests, pelvic exams, breast exams and mammograms. You should continue to schedule annual wellness appointments. Since you are at an increased risk for osteoporosis, providers usually recommend bone density screenings as well. Talk to your healthcare provider to determine how often you should make check-up appointments based on your health history.
What Can I Do To Prevent Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis isnt entirely preventable, but you can take steps to strengthen your bones. Eating foods high in calcium like cheese, yogurt, spinach or fortified cereals can help boost calcium intake. Adding a calcium supplement can also help. Some people also need a vitamin D supplement because it helps their body absorb calcium.
Also Check: Does Blue Cross Blue Shield Cover Testosterone
Getting Tested At Your Healthcare Providers Office
Your Symptoms May Be The Key
So how are you supposed to navigate this complex problem of estrogen testing?
The key may be in your symptoms.
The evaluation of your estrogen should always be in the setting of whatever symptoms you are experiencing.
You are the single best way to determine if your levels are normal or abnormal.
For instance:
If you KNOW that your cycle has been stable and normal for the last 5 years but suddenly it’s off by 1 week, there is definitely something wrong.
If you have previously not had any issues but you are now suffering from breast tenderness, migraines or mood issues related to your cycle, there is a high probability that something is wrong.
It’s often the case that your estrogen levels may show up “normal” even in the face of these types of symptoms.
For this reason, you should always pair up how you are feeling clinically with what your labs show.
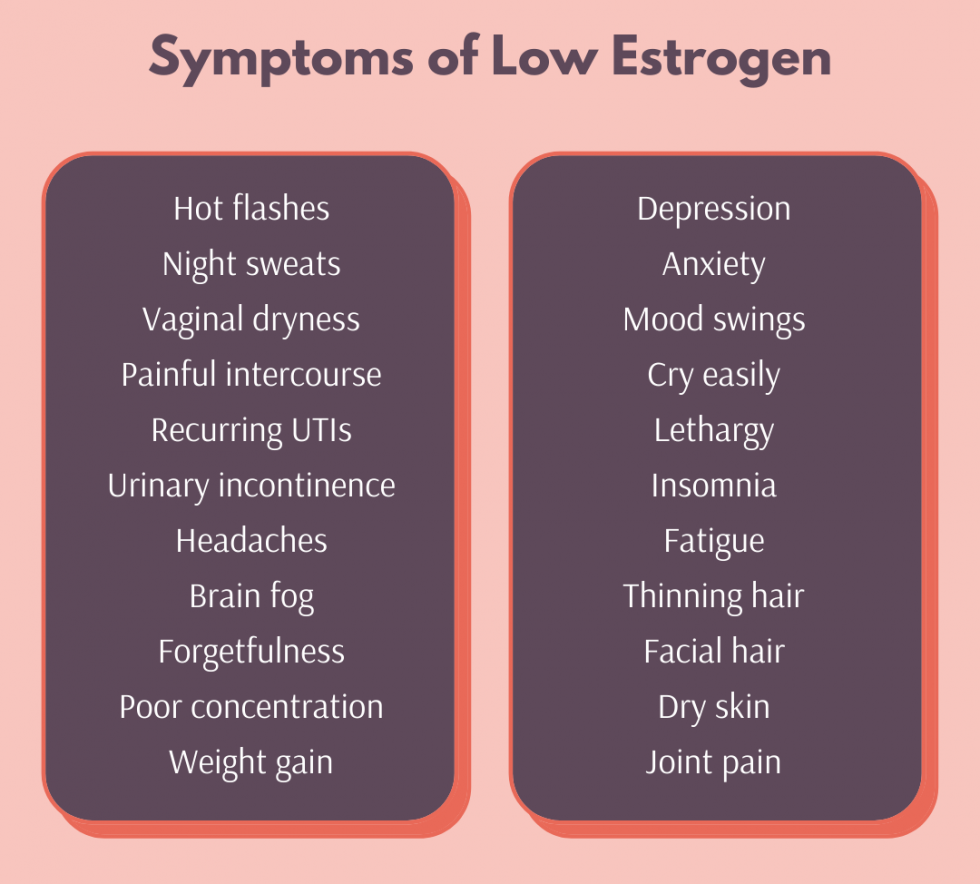
I’ve provided a list of symptoms which tend to be associated with high and low estrogen below:
Symptoms of Low Estrogen
Low estrogen is relatively unusual among young menstruating women and thus tends to be more common as women age.
The principal cause of low estrogen is menopause which tends to occur in the fifth decade of life.
Other conditions, such as the removal of ovaries or the use of anastrozole, can trigger menopausal-like symptoms in women and lead to symptoms of low estrogen as well.
You can find a list of low estrogen symptoms below:
You can read more about supplements designed to help manage low estrogen here.
Recommended Reading: How Long Does Olly Sleep Take To Work
When Estrogen Is Lower During The Late Luteal Phase And The Start Of The Period You May Notice Some Changes
-
Your overall body temperature will increase slightly during this phase.
-
One study found that 2 out of 5 women report more sensitive skin, which researchers suspect could be due to low levels of estrogen during this time .
-
Premenstrual symptoms also show up during this time before the period starts, when estrogen are low.
-
Some people may even get migraine headaches that are related to the drop in estrogen levels .
What Is High Or Low Estrogen Levels
Estrogen is a naturally occurring hormone that your body produces to aid in sexual development and other important body functions. Prior to menopause, women generate estrogen primarily from their ovaries. After that, most of their estrogen comes from fat cells and the adrenal glands found at the top of the kidneys. When estrogen levels get too high or too low, this can negatively affect the body.
Estrogen helps regulate the health of the following areas:
- Urinary tract
- Mucous membranes
- Brain
Estrogen plays an essential role in girls when they reach puberty, prompting changes like the growth of pubic hair and the start of menstruation. It also helps control cholesterol in the blood. Three of the most common types of estrogen produced in women include:
Estrone
Estrone is the main estrogen hormone produced by women after they hit menopause.
Estradiol
Estradiol is the primary estrogen hormone produced by non-pregnant women.
Estriol
Estriol is an estrogen hormone whose levels increase in pregnant women.
Don’t Miss: Does Melatonin Increase Estrogen
What Are Irregular Periods
Most women have menstrual cycles that last between 21 and 35 days. Up to one quarter of women experience irregular periods. This includes having periods that are shorter or longer than usual or periods that are lighter or heavier than usual. Some women who have irregular periods may experience abdominal cramping or a lack of ovulation. Amenorrhea is a medical term that refers to an absence of periods for at least 3 months even though a woman is not pregnant. Menorrhagia is the term that means excessive menstrual bleeding. Dysmenorrhea refers to pain and cramping during periods. Prolonged menstrual bleeding involves periods in which bleeding routinely lasts for 8 days or longer. Oligomenorrhea is a condition in which periods occur infrequently or more than every 35 days. See your doctor if you believe hormonal imbalance is affecting your menstrual cycle.
Why Estrogen And Progesterone Replacement Therapy Is Important
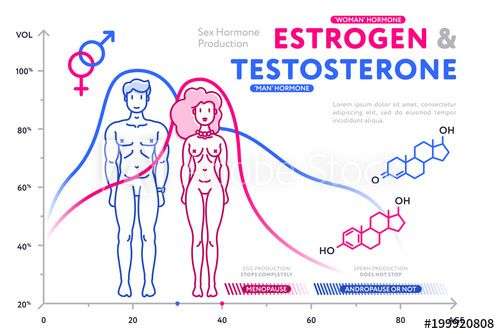
You might think that improving your levels of estrogen is mainly for the purpose of resolving menopausal symptoms. But actually, there is medical advice that suggests hormone therapy is even more important than that.
If your estrogen and progesterone levels arent properly balanced, you are at a higher risk for cancer. Additionally, low estrogen can put you at risk for weaker bones and even osteoporosis.
So, for many women, hormone therapy isnt just a question of improving their daily lives its a matter of health as well.
Also Check: Does Blue Cross Blue Shield Cover Bioidentical Hormone Therapy
Questions Talk To A Doctor Today
If youre concerned about your estrogen levels or just want to talk to an expert about your symptoms, its time to see a doctor.
Dade City and Wesley Chapel patients can with Dr. Ayazo or call . No matter your health concerns, Dr. Ayazo is here to answer your questions and work with you on a personalized plan to help you start feeling better.
What You Can Do About It
If you think you might have low estrogen, the first thing to do is talk to your doctor. They can test your hormone levels to make sure this is the case. Then they can work with you to figure out why this might be happening so you can get the correct treatment.
“If you have symptoms of low estrogen, you shouldn’t tough it out. There’s help for you!” Dr. Eyvazzadeh says. “And if you don’t have a doctor that is listening and paying attention to your symptoms then find another one. A gynecologist should be able to help with symptoms of low estrogen.”
It’s important, though, to rule out menopause as a factor. “If you suspect premature menopause, you do want to see your gynecologist, because women with premature menopause need to be on hormonal therapy,” says Dr. Minkin. “The rate of premature menopause is high enough that everyone should know how to check for it and the symptoms,” says Dr. Eyvazzadeh.
Having low estrogen isnât immediately dangerous per se but it definitely affects your bodyâs performance on a number of levels. If youâve read the symptoms and think your estrogen might be low, talk to your doctor about getting your levels tested. Your doctor can help you get your levels, and your life, back on track.
Studies Cited
Experts
Dr. Mary Jane Minkin, MD, clinical professor in the Department of Obstetrics, Gynecology, and Reproductive Sciences at the Yale University School of Medicine
Recommended Reading: How Much Is Estrogen Pills
The Function Of Estrogen
Estrogen is the hormone that’s mainly responsible for sexual development in girls as they reach puberty.
Other functions of estrogen include:
- Initiates changes in breast tissue during teenage years and pregnancy
- Helps regulate menstrual cycles
- Helps regulate body weight by helping to control metabolism
- Involved in the development and growth of healthy bone tissue
- Plays a role in promoting healthy cardiovascular health, according to the American Heart Association
How Do I Know My Estrogen Levels Are Low Or High
As estrogen levels do fluctuate regularly throughout the cycle, its difficult to pinpoint a typical or normal level of estrogen because they tend to change almost every day . In saying that, when estrogen levels fluctuate or become low, you may experience a number of signs and symptoms. This can occur for a number of reasons – from an underlying condition or things such as age, or the use of certain medications.
Some common indicators of hormonal imbalance include:
- Irregular periods, heavier or lighter periods, or total cessation of periods
- Weight gain or difficulty losing weight
- Feeling tired all of the time
- Mood changes
- Acne on the face, back or chest
- Hair growth on the face, chin and breasts
The most reliable way to check estrogen levels at home is with an at-home hormone test because its processed by a highly accredited network of laboratories. The process is simple:
Its recommended that you check your hormone levels if:
You May Like: Estrace Weight Gain
How Low Estrogen Can Affect Your Body
Estrogen is a very busy hormone for women throughout their lives. Men have some too, but women have more. Estrogen is primarily active in reproductive development and health for women, but its role is far greater than that.
Estrogen is actually a group of sex hormones, each of them performing different roles in womens health and development. Estrogen helps make women curvier than men by making their pelvis and hips wider, and their breast grow.
Estrogen is part of your menstrual cycle, helps you get pregnant, and plays a role in helping you develop bones and grow hair. It also helps regulate your moods and impacts your brain development and structure.
Hormonal Imbalance And Fatigue
Fatigue is a common symptom that may have many potential underlying causes. Just as too little progesterone can make it hard to sleep, too much progesterone can make you more tired. Another common hormonal imbalance that causes fatigue is low thyroid hormone levels . This condition is easily diagnosed with a blood test. If your levels are low, you can take prescription medication to bring your levels back up to normal. Regardless of any hormone imbalance that may exist, practice good sleep hygiene to optimize your sleep. This involves going to bed and waking up at the same time every day, even on the weekends. Avoid alcohol, caffeine, and exercise from the late afternoon on to avoid interfering with sleep. Establish a relaxing nighttime routine to give your body the message that it’s time for sleep. Take a warm bath, sip a cup of chamomile tea, or listen to relaxing music.
You May Like: Does Blue Cross Blue Shield Cover Trt
During The Follicular Phase Of The Cyclefrom The Start Of Your Period Until Ovulationestrogen Levels Are High You May Notice Some Changes Throughout Your Body
-
Just before ovulation, some people may notice that their skin and hair are less oily, though we donât know for sure that the increase in estrogen causes these changes .
-
Your cervical fluid changes throughout the follicular phase:
-
Early-to mid follicular: dry/sticky
-
Late follicular to ovulation: wet and slippery, like an egg white
-
Some people notice an increase in their sex drive around ovulation
Estrogen Levels During Pregnancy
Hormone production is really high during pregnancy. Estradiol skyrockets, along with other hormones like progesterone, testosterone, and prolactin . These hormones, plus many more, work together to support the development of a baby.
-
First trimester estradiol: 188â2497 pg/mL
-
Second trimester estradiol: 1278â7192 pg/mL
-
Third trimester estradiol: 3460â6137 pg/mL
Also Check: What Causes Breakthrough Bleeding When On Bioidentical Hormones
Low Sex Drive Could Be Low Testosterone
Testosterone is typically thought of as a male hormone, but both men and women have it. Low testosterone levels may cause low libido. In one study of more than 800 postmenopausal women reporting low sex drive, those who received 150 or 300 micrograms per day of testosterone in the form of a topical patch reported more sexual desire and less distress than women who received a placebo. Women receiving extra testosterone also reported more satisfying sexual experiences compared to women who took a placebo. However, women who took 300 micrograms of testosterone per day had more unwanted hair growth than women who took the placebo. Men can get low testosterone, too. The condition has been referred to as andropause in males.