Esr1 Structural Rearrangements And Esr1 Fusions
Using a PDX model to better understand endocrine therapy resistance, we previously reported a somatic gain-of-function event in the form of a chromosomal translocation identified in a patient presenting with aggressive endocrine therapy resistant, metastatic ER+ disease. This translocation produced an in-frame fusion gene consisting of exons 1-6 of ESR1 and the C-terminus of the Hippo pathway coactivator gene, YAP1 , thereby generating a stable ESR1 fusion protein that was a highly active constitutive transcription factor. Our group more recently discovered another in-frame ESR1 fusion gene involving the protocadherin 11 X-linked gene, PCDH11X provided by inter-chromosomal translocation that also produced stable ESR1 fusion protein identified in a patient with endocrine-refractory, metastatic ER+ breast cancer. In both ESR1-e6> YAP1 and ESR1-e6> PCDH11X fusions, the LBD of ESR1 is replaced with in-frame sequences from another gene, and therefore the drug binding domain that endocrine therapies recognize is absent. These two fusions promoted endocrine therapy resistant cell proliferation and constitutively activated ER target genes. Interestingly, both fusions also upregulated an epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition -like transcriptional signature, induced cell motility, and increased lung metastatic frequency. These results suggest that ESR1 fusions are able to drive not only endocrine therapy resistance, but also drive metastasis, linking these two lethal processes together.
Your Race And Ethnicity
Overall, white women are slightly more likely to develop breast cancer than African American women, although the gap between them has been closing in recent years. In women under age 45, breast cancer is more common in African American women. African American women are also more likely to die from breast cancer at any age. Asian, Hispanic, and Native American women have a lower risk of developing and dying from breast cancer.
Risk in different groups also varies by type of breast cancer. For example, African American women are more likely to have the less common triple-negative breast cancer.
Finding The Type Of Cancer
A pathologist looks at the cancer cells under a microscope to see which type of breast cancer it is. They can tell this by the shape of the cells and the pattern of the cells in the breast tissue.
Pathologists also sometimes use particular dyes to stain the cells and show up certain proteins or features of the cells.
Read Also: Does Blue Cross Blue Shield Cover Testosterone
What Is Estrogen Receptor
Estrogen is the female sex hormone responsible for the growth, development, and regulation of the female reproductive system and secondary sex organs.
The cells that respond to this hormone contain proteins that bind to it and bring about the required effect. These proteins are known as estrogen receptors and are found in female reproductive tissues and cancer cells.
Breast cancers that grow in response to estrogen due to the presence of estrogen receptors are known as estrogen receptor-positive or ER-positive breast cancer.
These cancers grow slower than ER-negative cancers and account for 80% of all breast cancers.
Risk Of Recurrence: Early And Late

Research has shown the HER2-positive early breast cancers are two to five times more likely to recur than HER2-negative tumors. Even very small HER2-positive tumors with negative lymph nodes have a much higher risk of recurrence relative to tumors that are HER2-negative. Treatment with Herceptin can cut this risk by half.
The pattern of breast cancer recurrence may also differ. Small tumors are also more likely to have a metastatic recurrence if they are HER2-positive.
Despite the fact that HER2-positive and estrogen receptor-negative tuors are more likely to recur early on than estrogen receptor-positive and HER2-negative cancers, late recurrences are much less common.
With estrogen receptor positive breast cancers, the cancer is more likely to recur after 5 years than in the first 5 years, and the risk of recurrence remains steady each year for at least 20 years following the diagnosis. In contrast, those who have HER2 positive tumors and reach their 5 year mark are much more likely to be “in the clear” and remain recurrence free.
Also Check: Does Nugenix Have An Estrogen Blocker
Concordance Of Hormone Receptor Status And Brca1/2 Mutation Among Women With Synchronous Bilateral Breast Cancer
- 1Department of Breast Surgery, Shanghai Cancer Center/Cancer Institute, Fudan University, Shanghai, China
- 2Department of Oncology, Shanghai Medical College, Fudan University, Shanghai, China
- 3Department of Radiation Oncology, Shanghai Cancer Center/Cancer Institute, Fudan University, Shanghai, China
Goals: BRCA1/2 mutations are associated with bilateral breast cancer. The extent of concordance between synchronous bilateral breast cancer tumors with respect to hormone receptor expression and BRCA1/2 mutations is unknown. We investigated the distribution of BRCA1/2 mutations and bilateral estrogen receptor status in SBBC.
Methods: A retrospective analysis was performed on 15,337 patients with primary breast cancer who underwent surgical treatment at the Fudan University Shanghai Cancer Center between 2007 and 2014. We included 163 patients with synchronous bilateral breast cancer who had germline BRCA1/2 mutations testing. BRCA1/2 pathogenic/likely pathogenic mutations and other clinicopathological characteristics were studied in further analyses.
Our study shows that Chinese women with SBBC have different characteristics from their UBC counterparts. SBBC patients with a younger age, family history of breast cancer, or bilateral ER-negative disease are more likely to have BRCA1/2 mutations. SBBC patients with a concordant ER-negative status had worse early outcomes. Our results suggest that there may be additional factors underlying the tumor biology and genetics of SBBC.
Is Colon Cancer Hereditary
Colon cancer is a malignancy that begins in the colon, or in the large intestine. It is known to start forming as benign polyps flat, or knob-shaped growths that are present on the inner
lining of the large intestine. Occasionally, these growths are known to cause symptoms such as unexplained bleeding , or constipation. However, in most cases, these polyps produce no early symptoms at all which is why most people may not even realise when these signs are present.
Some polyps may continue to remain benign, which means that they will exist as non-cancerous masses. Some of these tumours can become malignant, or cancerous. These polyps are often detected using a procedure called a colonoscopy.
Don’t Miss: Can Having Your Tubes Tied Cause Hormonal Imbalance
Differences In The Clinicopathological Characteristics Of Patients With Sbbc And Ubc
A total of 15,337 patients with primary breast cancer underwent surgery at the Fudan University Shanghai Cancer Center between 2007 and 2014. One hundred and sixty-three SBBC patients with germline BRCA1/2 testing and integral clinicalpathological information in the same period was included. Patients treated for metachronous bilateral breast cancer , male patients and stage IV patients who underwent palliative operations during the same time period were excluded from the study. Locally advanced patients, such as those with stage IIIb or IIIc disease, were excluded from the present study to avoid the risk of misclassifying metastatic bilateral breast cancer.
As shown in Table 1, patients with SBBC developed malignant carcinoma at an older age than patients with UBC . Compared with the 9.6% of UBC patients who had a family history of breast cancer, 11.7% of patients with SBBC had a similar family history within first-degree relatives. In contrast, 14.1% of SBBC patients had carcinomas with a lobular component in either breast based on pathological reports . There was no significant difference in TNM stage distribution. However, SBBC patients tended to have received bilateral mastectomy, and only 8.0% of SBBC patients chose breast-conserving surgery or breast reconstruction compared with 24% of UBC patients . ER-positive carcinoma was more often found in SBBC patients than in UBC patients , and HER2 status was similar in both groups.
Risks For Breast Cancer
A risk factor is something that increases the risk of developing cancer. It could be a behaviour, substance or condition. Most cancers are the result of many risk factors. But sometimes breast cancer develops in women who dont have any of the risk factors described below.
Most breast cancers occur in women. The main reason women develop breast cancer is because their breast cells are exposed to the female hormones estrogen and progesterone. These hormones, especially estrogen, are linked with breast cancer and encourage the growth of some breast cancers.
Breast cancer is more common in high-income, developed countries such as Canada, the United States and some European countries. The risk of developing breast cancer increases with age. Breast cancer mostly occurs in women between 50 and 69 years of age.
Don’t Miss: Can Having Your Tubes Tied Cause Hormonal Imbalance
Is Stomach Cancer Hereditary
Stomach cancer is the second leading cause of cancer related deaths worldwide and in India, the fourth in the list of the most common cancers. As per the US National Institutes of Health close to ten percent of stomach cancer cases have a familial origin. Having a first degree relative such as father, mother, brother or sister with stomach cancer increases the risk of developing stomach cancer.
While gene mutations have been linked to stomach cancer in some people, the exact genetic factors are not fully understood. Scientists believe a combination of environmental and genetic factors could be responsible for familial stomach cancer.
Some of the inherited conditions that increase stomach cancer risk include:
Hereditary diffuse gastric cancer :
This is an inherited, rare condition that increases risk of stomach cancer caused by a mutation in a gene known as CDH1.
Diffuse gastric cancer also known as or linitis plastica orsignet ring cell gastric cancer affects almost the entire stomach rather than any one specific area in the stomach. According to the NIH, diffuse gastric cancers account for 20 percent of stomach cancers and HDGC is responsible for a small amount of these cancers. Women diagnosed with HDGC are at an increased risk of developing breast cancer.
Diagnosis of HDGC is made if any one criteria listed below are met apart from recommending CDH1 genetic testing:
Lynch syndrome:
Familial adenomatous polyposis:
BRCA gene mutations:
Li-Fraumeni syndrome:
Mechanisms And Therapeutic Vulnerabilities Of Breast Cancers Harboring Esr1 Point Mutations
Structural analysis has revealed that the formation of hydrogen bonds between S537 or G538 and D351 located within helix 12 of ESR1 LBD confers an agonist conformation to ESR1 mutant proteins. In wild-type ER, the binding of ligand alters the position of helix 12 into an open pocket, favoring recruitment of transcriptional coactivators such as p160 family members that include SRC-3, and histone acetylases CBP and p300. In contrast, tamoxifen results in disposition of helix 12 that hinders coactivators binding and results in recruitment of corepressors such as N-CoR/SMRT. The substitution of D538 to glycine mimics the active conformation of wild-type ER bound by estrogen.
The development of sequencing technologies and the various models to recapitulate ESR1 mutant bearing tumors allow insightful studies into the landscape and targeted therapies of activating point mutations in the ESR1 LBD. Further studies are needed to address the use of ESR1 mutations as predictive biomarkers to stratify patient subsets and predict ESR1 mutation specific therapeutic vulnerabilities.
You May Like: Does Nugenix Have An Estrogen Blocker
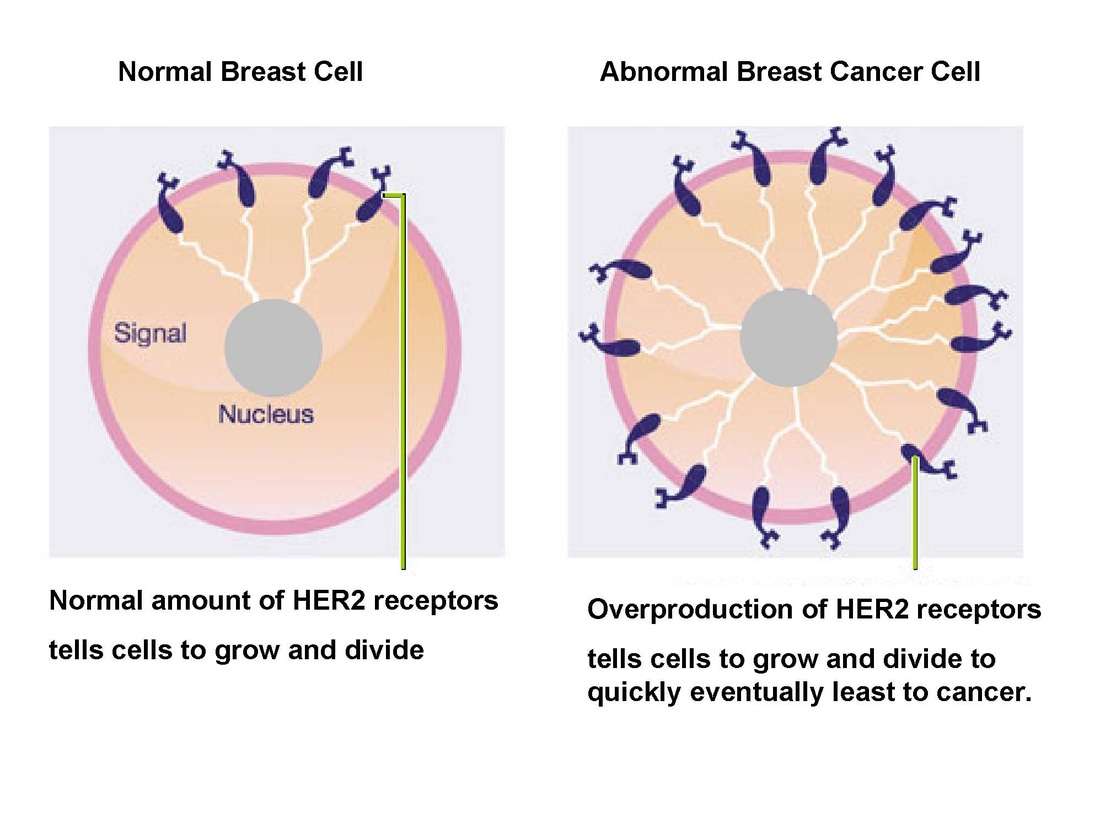
Determining Your Her2 Status
A breast biopsy is used to determine HER2 status. The biopsy can be sent for laboratory testing with an immunohistochemistry test. The fluorescence in situ hybridization test looks for the HER2 gene in breast cancer cells.
The results of an immunohistochemistry test show different levels of HER2 positivity. For example, a tumor may be reported as 0, 1+, 2+, or 3+. Tumors with a higher number may be referred to as having an overexpression of HER2.
According to the American Cancer Society, immunohistochemistry test results should be considered as follows:
| Designation | |
|---|---|
| Equivocal | |
| 3+ | HER2-positive |
The impact of being HER2-positive on breast cancer survival is, of course, a top concern. Unfortunately, statistics can be misleading without considering other aspects of your diagnosis, including cancer stage at diagnosis and whether the tumor is also estrogen and/or progesterone receptor-positive.
With this in mind, you may also be tested for progesterone and estrogen receptors. Triple-negative breast cancers are negative for HER2, estrogen, and progesterone, while triple-positive breast cancers are positive for all three.
Whole Exome Sequencing Reveals Unique Mutations In Ethiopian Breast Tumors
We performed DNA sequencing on three tumors and healthy tissue from matched patients. Each of the three tumors were identified as ER+ using immunohistochemical subtyping. We identified mutations in 615 genes across all three patients, unique to the tumor tissue . Two patients had a mutation in a different spot in the BRCA2 gene, which is not surprising based on the number of variants of uncertain significance in BRCA2 .
Additionally, data from this population shows that patients with a family history were more likely to be ER-than patients without a family history , suggesting that many of these patientsâ cancers are due to somatic mutations. We also searched for mutations in genes related to breast cancer aggression, subtype, and progression. Gene ontology enrichments showed MSigDB Oncogenic categories related to KRAS, PTEN, and EGFR signaling , demonstrating that at least some of the somatic variants in population are in the same pathways as other ER + tumors in other populations .
GSEA enrichments of the SNPs found across the Ethiopian patient tumors.
Read Also: Does Melatonin Cancel Out Birth Control Implant
Ethiopian Women Present With Aggressive Er1 Breast Cancer At A Young Age
Through discussions with surgeons and oncologists at the Black Lion Hospital in Addis Ababa, we were alerted to the fact that Ethiopian women are diagnosed at a much younger age than women of European descent. A recent study found that the overall mean age at diagnosis was 43 years old, and 40% of patients were under 40 years old . Amongst this cohort, patients with Luminal B breast cancer had the youngest median age at diagnosis at 35, followed by Her2-enriched at 41, Triple negative at 46, and Luminal A at 47. The age of diagnosis across breast cancer subtypes is consistently younger for those born in Africa compared to those born in the US . Also, at the time of diagnosis, Ethiopian patients had a significantly higher chance of having a higher-grade pathology compared to White and African Americans, across all subtypes . Second, a recent study from Jemal and Fedewa demonstrated that breast cancer cases in East Africa are more likely to be ER+ compared to West African or African American cases .
a) Data from world health organization on mortality data across populations from Ethiopia , Ghana , Nigeria and US . b) Data adapted from Jemal and Fedewa on age of diagnosis of breast cancer across relevant subpopulations . c) Proportion of ER+ breast cancer patients from the same reference.
The Impact On Breast Cancer Treatment
You might be wondering why someone who already has cancer would consider BRCA testing, but genetics can play an important role when determining treatment options.
If you have breast cancer and test positive for a BRCA mutation, your treatment options could potentially change. Heres what you need to know:
- Some women with breast cancer are resistant to standard cancer treatments, such as chemotherapy, making them less effective
- Even if the cancer does respond to treatment, it can eventually return
- People with breast cancer and a BRCA mutation have tumor cells that struggle to repair DNA damage in a certain way
- Because of this, these cells rely more heavily on other ways to repair DNA damage, like using an enzyme called PARP
- When PARP is stopped from repairing DNA damage, cancer cells struggle even more to repair DNA damage and are more likely to die
- Knowing if you have ER-positive, PR-positive, HER2-positive, HER2-negative, or triple-negative breast cancer could determine treatment eligibility for certain therapies
Talk to your doctor about getting BRCA tested early. Knowing that you have a mutation could help determine treatment options.
- ER-positive=estrogen receptor-positive.
- HER2-negative=human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative.
- HER2-positive=human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive.
- PARP=poly polymerase.
Recommended Reading: Does Kaiser Cover Hormone Replacement Therapy
Frequent Esr1 Point Mutations In Endocrine
Advances in sequencing technologies have allowed more sensitive detection and thus insights into the landscape of ESR1 LBD point mutations in both primary and metastatic ER+ breast tumors. Three ESR1 mutations, Y537S, Y537N, and D538G were identified by next-generation sequencing in 14 out of 80 patient samples with endocrine-refractory, metastatic ER+ breast cancer. Notably, all breast tumors from patients that were found to harbor ESR1 LBD point mutations were treated with AIs. Interestingly, these alterations were not detected in matched primary samples and were also not detected in separate large sets of treatment naïve patients. Analysis of an independent ER negative cohort also failed to detect any ESR1 point mutations in the LBD. Although ESR1 mutations were found in 3% of primary samples in this population, alterations in Y537 and D538 residues of ESR1 were enriched in patients treated extensively with AIs. These results suggest that these ESR1 LBD mutations are acquired, or detected, in patients after treatment with endocrine therapy.
Breast Cancer Research At Moffitt Cancer Center
Moffitt Cancer Center has been designated a Comprehensive Cancer Center by the National Cancer Institute, an achievement that speaks directly to our commitment to advancing research and treatment for this malignancy. We are researching the causes of HER2 positive breast cancer every day, and we wont be satisfied until there is a cure. To advance the treatment of this malignancy, Moffitt spearheads a robust clinical trials program where eligible patients can receive the latest breakthroughs in treatment before they are available elsewhere.
If you would like to learn more about the causes of HER2 positive breast cancer, or if you have been diagnosed with this malignancy and would like to explore the treatment options available to you at Moffitt, we encourage you to request an appointment. To do so, call or submit a new patient registration form. We accept patients with or without referrals.
- BROWSE
Read Also: Can Having Your Tubes Tied Cause Hormonal Imbalance