How Can Hormones Affect The Growth Of Breast Cancer
Hormones like estrogen and progesterone are chemicals produced by glands in the body. Normally, these hormones help regulate body cycles, like menstruation. However, sometimes these same hormones can cause cancer to grow.
The pathologist will perform tests on the breast cancer cells to determine if they have receptors that feed on estrogen or progesterone, stimulating their growth. If the cancer cells have these receptors, your doctor may recommend hormone therapy drugs, such as blockers or inhibitors. Both types of drugs help to destroy cancer cells by cutting off their supply of hormones.
Treating Stage Iii Breast Cancer
In stage III breast cancer, the tumor is large or growing into nearby tissues , or the cancer has spread to many nearby lymph nodes.
If you have inflammatory breast cancer: Stage III cancers also include some inflammatory breast cancers that have not spread beyond nearby lymph nodes. Treatment of these cancers can be slightly different from the treatment of other stage III breast cancers. You can find more details in our section about treatment for inflammatory breast cancer.
There are two main approaches to treating stage III breast cancer:
Herbs And Supplements During Menopause
Many over-the-counter natural products are promoted in stores and online as helpful with menopausal symptoms. These include vitamins and soy-based and herbal products . There are also endless arrays of special blends of herbs and vitamins that claim to reduce the discomforts of menopause.
These products are considered dietary supplements . They have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration to be sure that they work or even that they are safe. Some supplements have been tested in small clinical trials, but often the studies only looked at taking the substance for a short time , so it isnt clear how safe it would be if taken for a long time. Another concern has been applying the results of a study of a particular version and dose of a supplement to others that werent tested.
Most of the plain herbs that are touted for menopausal symptoms carry a low risk of harm for most women, but some can interact with other drugs and/or cause unexpected problems. You should discuss herbs or supplements with your doctor before taking them.
Well-controlled scientific studies are needed to help find out if these products work and if they are any safer than the hormone therapy drugs now in use.
You can learn more in Dietary Supplements: What Is Safe?
Don’t Miss: Estradiol And Progesterone Side Effects
Types Of Hormone Treatment
Medicines include:
- Selective estrogen receptor modulators . Examples are raloxifene and tamoxifen . These drugs block the receptors on the surface of cancer cells.
- Aromatase inhibitors. These drugs include anastrozole , exemestane , and letrozole . These block the enzyme aromatase, which converts other hormones to estrogen. They are used mostly in women who are past menopause.
- GnRH agonists or LH-RH agonists. These drugs include goserelin and leuprolide . They stop your ovaries from making estrogen.
- Fulvestrant . This drug changes the receptors so that they can’t take in estrogen.
Hormone treatment sometimes involves surgery to remove the ovaries or radiation treatments to the ovaries. The goal is to stop the ovaries from making estrogen.
Side effects of hormone medicines
Side effects depend on the drug that is used.
Side effects of surgery
- Removing your ovaries makes you start menopause, if you haven’t started it already. Menopause often has symptoms like hot flashes, vaginal dryness, urinating often, and having less interest in sex. And it raises your risk for other diseases, like heart disease and osteoporosis.
- When your ovaries are removed, you can no longer get pregnant.
Managing side effects
Some hormone treatments cause menopause symptoms like vaginal dryness, mood swings, and hot flashes. If you have mild symptoms, you may get some relief if you eat healthy foods, exercise, and lower your stress.
Who Gets Hormone Therapy For Breast Cancer
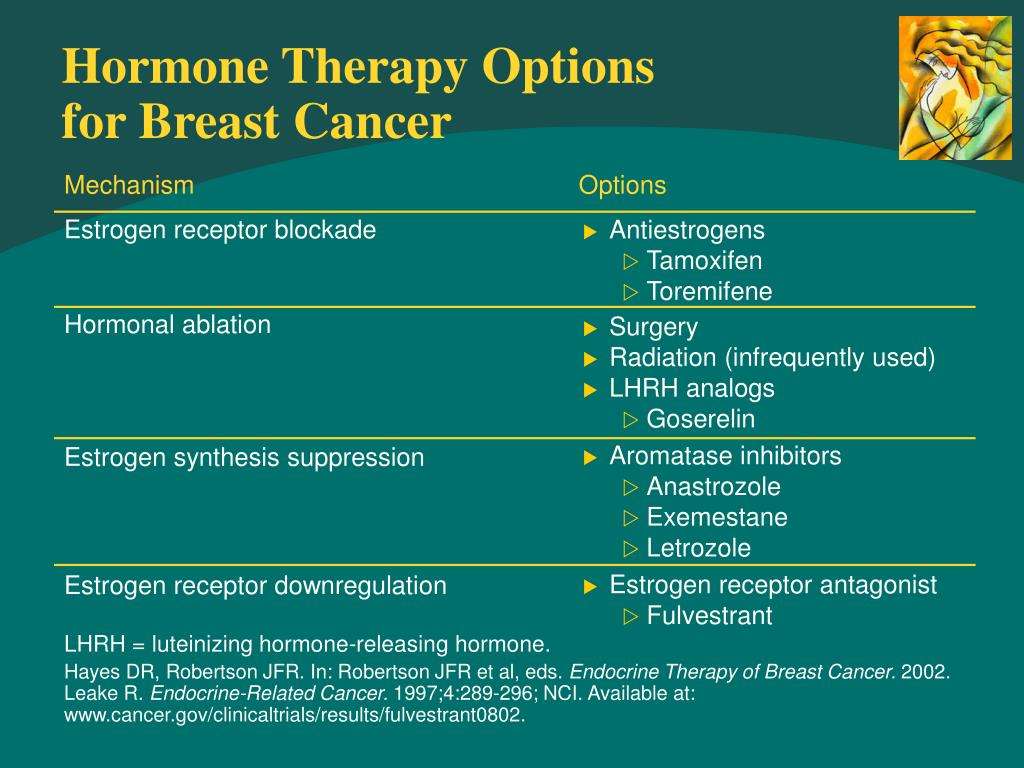
When youâre diagnosed with breast cancer, your doctor will test cells from your tumor to see if they have parts on their surfaces called receptors that use estrogen or progesterone. If they do, it means that they depend on these hormones to grow. In that case, your doctor will probably recommend hormone therapy as part of your treatment plan.
If youâve already been treated for breast cancer, you might use hormone therapy to help keep it from coming back. It also helps lower your odds of getting new cancers in the other breast.
Also, if you don’t have the disease but have a family history of it, or genes that raise your risk, your doctor may recommend hormone therapy to lower your chances of getting it.
You May Like: Can Estrace Cause Weight Gain
Looking After Your Bones While Taking An Aromatase Inhibitor
Aromatase inhibitors can reduce bone density. This may increase the risk of breaks in the bones. To keep your bones healthy while you are taking this medication, your doctor may recommend that you:
- have a bone density test before and during treatment
- do regular weight-bearing exercise
- maintain a healthy intake of calcium
- ensure a healthy intake of vitamin D
- take other prescription medications to build up your bones if your bone density is already low
If you do show signs of bone thinning or weakening you may need to see your GP or specialist for special treatment for your bones.
What Are Hormone Inhibitors And How Do They Work
Hormone inhibitors also target breast cancer cells with hormone receptors, but unlike hormone blockers, they work by reducing the bodys hormone production. When breast cancer cells are cut off from the food supply the tumor begins to starve and die.Generally, the benefits of using hormone therapy and chemotherapy together have a much greater combined effect than using either alone. If your breast cancer is positive for hormone receptors, your doctor may recommend both therapies.
You May Like: Can Getting Your Tubes Tied Cause Early Menopause
Estrogen Therapy And Cancer Risk
Endometrial cancer
In women who still have a uterus, using systemic ET has been shown to increase the risk of endometrial cancer . The risk remains higher than average even after ET is no longer used. Although most studies that showed an increased risk were of women taking estrogen as a pill, women using a patch or high-dose vaginal ring can also expect to have an increased risk of endometrial cancer.
Because of this increased cancer risk, women who have gone through menopause and who still have a uterus are given a progestin along with estrogen. Studies have shown that EPT does not increase the risk for endometrial cancer.
Long-term use of vaginal creams, rings, or tablets containing topical estrogen doses may also increase the levels of estrogen in the body. Its not clear if this leads to health risks, but the amounts of hormone are much smaller than systemic therapies.
Breast cancer
ET is not linked to a higher risk of breast cancer. In fact, certain groups of women taking ET, such as women who had no family history of breast cancer and those who had no history of benign breast disease, had a slightly lower risk of breast cancer.
Ovarian cancer
The WHI study of ET did not report any results about ovarian cancer.
To put the risk into numbers, if 1,000 women who were 50 years old took estrogen for menopause for 5 years, one extra ovarian cancer would be expected to develop.
Colorectal cancer
Lung cancer
ET does not seem to have any effect on the risk of lung cancer.
Hormone Therapy & The Treatment Of Breast Cancer
What Are Hormones?
Hormones are chemical messengers that regulate specific functions in the body, such as reproduction. Hormones are produced by many glands in the body and enter the bloodstream, where they travel to other tissues.
What Is Hormone Therapy & Who Can Benefit From It?
Hormone therapy is used in cancer treatment to increase or interfere with the activity of certain hormones that can influence the growth of tumors. Many breast cancers are hormone-sensitive, meaning that they may be estrogen receptor positive or progesterone receptor positive, depending on which hormone they react to. If a breast cancer is hormone sensitive, the hormones estrogen or progesterone can bind to cancer cells and stimulate growth and division. Hormone therapy prevents these hormones from binding to the cancer cells, stopping the cells from growing, and in doing so, preventing or delaying breast cancer recurrence. Hormone therapy can also lower the risk of a second, independent breast cancer.
What Are The Different Approaches To Hormone Therapy?
The goal of hormone therapy is to prevent hormones from attaching to cancer cells and helping cancer grow. This may be done in a number of ways, including:
Hormone therapy may include:
Is Hormone Therapy is Right for Me?
If you would like to learn more about hormone therapy or have cancer questions, call askSARAH at to speak to a nurse available 24/7.
Don’t Miss: Blue Cross Blue Shield Trt
How Does Hormone Therapy Work
About 2 out of 3 breast cancers are hormone receptor-positive. Their cells have receptors for the hormones estrogen and/or progesterone which help the cancer cells grow and spread.
There are several types of hormone therapy for breast cancer. Most types of hormone therapy either lower estrogen levels or stop estrogen from acting on breast cancer cells.
Estrogen Positive Breast Cancer Foods To Avoid
- The letter T followed by a number from 0 to 4 describe the tumor size and extent of the spread to the skin or chest wall under the breast. High T means the figures larger tumor and/or a wider spread to tissues around the breast.
- The letter N followed by a number from 0 to 3 indicates whether the cancer has spread to lymph nodes near the breast and, if so, how many lymph nodes are affected.
- The letter M followed by 0 or 1 indicates whether the cancer has spread to distant organs for example, lungs or bones.
What is the conventional treatment?
Foods to Avoid with Estrogen Dominance
You May Like: Does Melatonin Cancel Out Birth Control Implant
Less Common Types Of Hormone Therapy
Some other types of hormone therapy that were used more often in the past, but are rarely given now include:
- Megestrol acetate , a progesterone-like drug
- Androgens
- High doses of estrogen
These might be options if other forms of hormone therapy are no longer working, but they can often cause side effects.
What Types Of Hormone Therapy Are Used For Breast Cancer
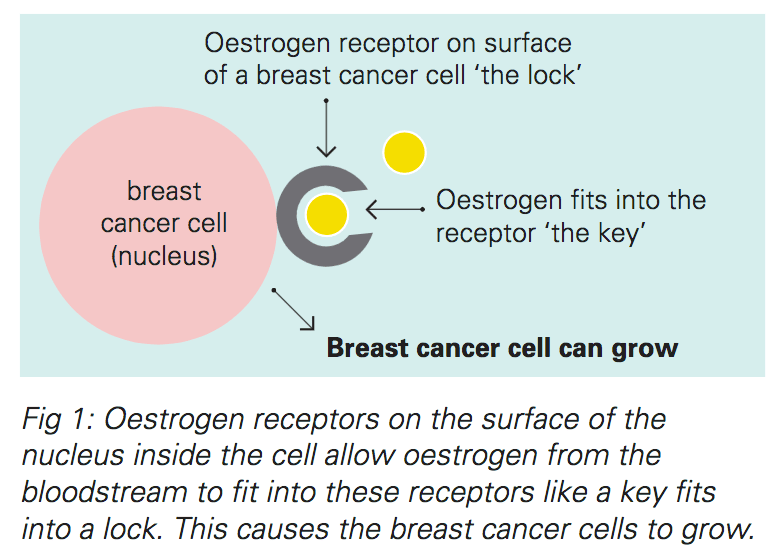
Several strategies are used to treat hormone-sensitive breast cancer:
Blocking ovarian function: Because the ovaries are the main source of estrogen in premenopausal women, estrogen levels in these women can be reduced by eliminating or suppressing ovarian function. Blocking ovarian function is called ovarian ablation.
Ovarian ablation can be done surgically in an operation to remove the ovaries or by treatment with radiation. This type of ovarian ablation is usually permanent.
Alternatively, ovarian function can be suppressed temporarily by treatment with drugs called gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists, which are also known as luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone agonists. By mimicking GnRH, these medicines interfere with signals that stimulate the ovaries to produce estrogen.
Estrogen and progesterone production in premenopausal women. Drawing shows that in premenopausal women, estrogen and progesterone production by the ovaries is regulated by luteinizing hormone and luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone . The hypothalamus releases LHRH, which then causes the pituitary gland to make and secrete LH and follicle-stimulating hormone . LH and FSH cause the ovaries to make estrogen and progesterone, which act on the endometrium .
Examples of ovarian suppression drugs that have been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration are goserelin and leuprolide .
You May Like: Does Nugenix Have An Estrogen Blocker
Womens Health Initiative Studies Of Hormone Therapy And Cancer Risk
Several large studies have looked at possible links between systemic hormone therapy in menopausal women and different types of cancer.
The main randomized studies of MHT were part of the Womens Health Initiative . The WHI included 2 randomized placebo-controlled clinical trials of MHT in healthy women:
- One study looked at estrogen therapy in post-menopausal women who didnt have a uterus. Over 5,000 women in the ET group took a daily dose of estrogen in the form of conjugated equine estrogen for an average of about 6 years. The researchers then continued to follow them for several years to look for any further effects of the hormone. The women were compared to more than 5,000 in the placebo group.
- The other study looked at estrogen-progestin therapy in post-menopausal women who still had their uterus. Over 8,500 women in the EPT group took a daily dose of CEE plus a progestin called medroxyprogesterone acetate for an average of about 5 years. This group was compared to a group of more than 8,000 women in the placebo group.
The WHI also conducted some observational studies. However, when we mention a WHI study below, were referring to one of the randomized studies.
Treatments For Breast Cancer
If you have breast cancer, your healthcare team will create a treatment plan just for you. It will be based on your health and specific information about the cancer. When deciding which treatments to offer for ductal carcinoma and lobular carcinoma, your healthcare team will consider:
- the stage
- if you have reached menopause
- the hormone receptor status of the cancer
- the HER2 status of the cancer
- the risk that the cancer will come back, or recur
- your overall health
You May Like: Estradiol Patch Price
Ovarian Ablation Or Suppression
For women who havent gone through menopause, ovarian ablation may be an option. This can be done medically or surgically. Either method stops estrogen production, which inhibits growth of cancer.
Surgical ablation is done by removing the ovaries. Without production of estrogen from the ovaries, you will enter permanent menopause.
How Hormone Therapy Is Given
Hormone therapy may be given in many ways. Some common ways include:
- Oral. Hormone therapy comes in pills that you swallow.
- Injection. The hormone therapy is given by a shot in a muscle in your arm, thigh, or hip, or right under the skin in the fatty part of your arm, leg, or belly.
- Surgery. You may have surgery to remove organs that produce hormones. In women, the ovaries are removed. In men, the testicles are removed.
You May Like: Does Nugenix Have An Estrogen Blocker
Menopausal Hormone Therapy And Cancer Risk
For decades, women have used hormone therapy to ease symptoms of menopause, such as hot flashes and sweating. This is called menopausal hormone therapy, and you may see it abbreviated as HT or MHT. You may also hear it described as hormone replacement therapy , postmenopausal hormone therapy , or postmenopausal hormones .
In the past, many doctors and their patients believed that MHT didnt just help with hot flashes and other symptoms it had important health benefits. But well-conducted studies have led many doctors to conclude that the risks of MHT often outweigh the benefits.
This information covers only how MHT can affect a womans risk of getting certain cancers. It does not cover other possible risks of MHT such as heart disease or stroke.
You can use this information when you talk to your doctor about whether MHT is right for you.
Hormone Therapy For Breast Cancer
Some types of breast cancer are affected by hormones, like estrogen and progesterone. The breast cancer cells have receptors that attach to estrogen and progesterone, which helps them grow. Treatments that stop these hormones from attaching to these receptors are called hormone or endocrine therapy.
Hormone therapy can reach cancer cells almost anywhere in the body and not just in the breast. It’s recommended for women with tumors that are hormone receptor-positive. It does not help women whose tumors don’t have hormone receptors.
You May Like: Does Nugenix Have An Estrogen Blocker
How Long Do I Take Tamoxifen
The American Society of Clinical Oncology recommends that:
- newly diagnosed premenopausal and perimenopausal women take 5 years of tamoxifen as their first hormonal therapy after this first 5 years is done, the hormonal therapy taken for the second 5 years would be determined by the womans menopausal status:
- postmenopausal women could take another 5 years of tamoxifen or switch to an aromatase inhibitor for 5 years
- pre- and perimenopausal women would take another 5 years of tamoxifen
British Columbia Specific Information
Breast cancer is the most common type of cancer in women in British Columbia. Breast cancer can occur in men as well, but it is not as common. Tests and treatments for breast cancer vary from person to person, and are based on individual circumstances. Certain factors such as your age, family history, or a previous breast cancer diagnosis may increase your risk of developing breast cancer. For information about your specific risk factors, speak with your health care provider.
A number of screening methods, including mammograms in women, can help find and diagnose breast cancer. The decision to have a mammogram or use any other screening method may be a difficult decision for some women. While screening for breast cancer is often recommended, it is not mandatory. Speak with your health care provider for information regarding how to get screened, the facts and myths about screening tests, how to maintain your breast health, and to get help making an informed decision.
For more information about breast cancer and breast cancer screening, visit:
If you have questions about breast cancer or medications, speak with your health care provider or call 8-1-1 to speak with a registered nurse or pharmacist. Our nurses are available anytime, every day of the year, and our pharmacists are available every night from 5:00 p.m. to 9:00 a.m.
Recommended Reading: Tubal Ligation Cause Early Menopause