Which Blood Tests & Lab Values Does Prednisone Change
- Sodium
- Eosinophils
- Platelets
If youve already been following me for a while you may have seen the nutrients which are depleted by prednisone as shown below. It shows that prednisone depletes calcium, chromium, and other vitamins. Were going to focus on a few of those and show how prednisone changed my personal lab values.
Impact Of Human Growth Hormone On Hypoglycemia
Adults with growth hormone deficiency can benefit from HGH therapy on many levels. Human growth hormone injections reverse the symptoms of GH deficiency. After exploring the question of does HGH cause hypoglycemia, we see that low growth hormone levels can cause too much insulin to deplete glucose in the bloodstream.
For further information about growth hormone deficiency and hypoglycemia, please contact Nexel Medical for a confidential, no-cost consultation.
*HGH therapy can help improve symptoms of both hypo and hyperglycemia.
Low Blood Sugar Level Causes
Most low blood sugar level causes are preventable and are caused due to a persons lifestyle and diet habits. Low blood sugar is common among diabetic patients who take medications to increase insulin levels.
All of the above causes are risk factors that may or may not be able to be inhibited. They are important to be aware of and act accordingly to keep yourself from getting a too high or too low blood sugar level.
If a person has medical, lifestyle or diet habits that cause irregular blood sugar levels, symptoms will begin to develop along with the drop or spike in blood sugar, and are as follows:
Don’t Miss: Does Nugenix Have An Estrogen Blocker
What Are Blood Sugar Levels
Blood sugar levels, also known as blood glucose level, is the level of sugar/glucose present in the blood. Glucose is a simple version of sugar which comes from the food we eat. Therefore, the more food you consume with high sugar levels over a period of time, will typically increase your blood sugar level.
Glucose comes from the foods we eat and its sugar content. When a person consumes a food with high sugar content, that is turned into glucose. The glucose is then absorbed into the bloodstream with the support of insulin. This is then distributed between the bodys cells and used as energy.
Foods high in glucose include most carbohydrates and a handful of proteins and fats. Most foods contain glucose as it is simply a natural sugar that occurs in most dietary forms. However, it is carbohydrates that contain the most sugar and 100% of it turns into glucose, through the process mentioned above, once consumed. The concentration of glucose present in the blood will determine your blood sugar level.
Here is a quick video explaining Blood sugar levels chart :
Your blood sugar level can either be low, normal or high. Depending on what you eat and health conditions, it will vary from person to person. Here is a breakdown of how your blood sugar works and how low or high blood sugar levels happens:
How The Liver Regulates Blood Glucose
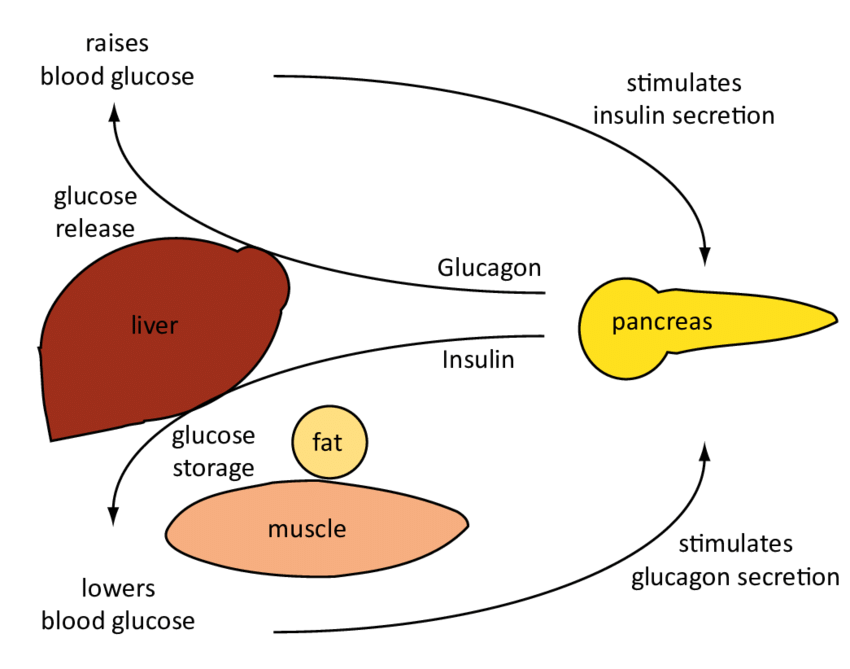
During absorption and digestion, the carbohydrates in the food you eat are reduced to their simplest form, glucose.
Excess glucose is then removed from the blood, with the majority of it being converted into glycoge, the storage form of glucose, by the livers hepatic cells via a process called glycogenesis.
Don’t Miss: Blue Cross Blue Shield Trt
Healing Steroids And Diabetes
Common steroids, such as prednisone and cortisone, help to reduce inflammation and swelling and are used to treat a variety of ailments ranging from arthritis, allergic reactions, respiratory issues and sinus infections, lupus, some cancers, to muscle spasms.
These steroids, known as glucocorticoids, are different from testosterone-based anabolic steroids that some people use to build muscle. The name is derived from glucose + cortex + steroid and refers to the fact that they play a role in the regulation of glucose metabolism.
These steroids are found in oral pill or tablet form, a liquid or cream solution, nasal inhaler, injections, or even intravenous therapy , depending on the medical treatment in question.
For PWDs who may be experiencing complications like trigger finger or frozen shoulder, these oral and injected steroid medications are often a common treatment option. But they come with serious side effects to your blood glucose control.
Per Scheiner, injections tend to have the most significant impact on BGs, while topical creams are less likely to have a glucose effect, though you can find some scattered anecdotes of that happening around the online community.
We see it all the time. Often, people dont realize theres cortisone or another type of steroid in . Or, healthcare professionals believe there isnt enough to affect blood sugars, says Dr. David S. Bell, a longtime endocrinologist practicing outside of Birmingham, Alabama.
What Happens If I Have Too Much Insulin
If a person accidentally injects more insulin than required, e.g. because they expend more energy or eat less food than they anticipated, cells will take in too much glucose from the blood. This leads to abnormally low blood glucose levels . The body reacts to hypoglycaemia by releasing stored glucose from the liver in an attempt to bring the levels back to normal. Low glucose levels in the blood can make a person feel ill.
The body mounts an initial ‘fight back’ response to hypoglycaemia through a specialised set of of nerves called the sympathetic nervous system. This causes palpitations, sweating, hunger, anxiety, tremor and pale complexion that usually warn the person about the low blood glucose level so this can be treated. However, if the initial blood glucose level is too low or if it is not treated promptly and continues to drop, the brain will be affected too because it depends almost entirely on glucose as a source of energy to function properly. This can cause dizziness, confusion, fits and even coma in severe cases.
Some drugs used for people with type 2 diabetes, including sulphonylureas and meglitinides , can also stimulate insulin production within the body and can also cause hypoglycaemia. The body responds in the same way as if excess insulin has been given by injection.
You May Like: Does Estrogen Cream Help Lichen Sclerosus
Manage Your Carb Intake
Your body breaks carbs down into sugars , and then insulin helps your body use and store sugar for energy.
When you eat too many carbs or have insulin-function problems, this process fails, and blood glucose levels can rise.
However, there are several things you can do about this.
The American Diabetes Association recommends managing carb intake by counting carbs and being aware of how many you need .
Some studies find that these methods can also help you plan your meals appropriately, further improving blood sugar management (
The recommended daily intake of fiber is about 25 grams for women and 38 grams for men. Thats about 14 grams for every 1,000 calories .
Summary
Eating plenty of fiber can help with blood sugar management. Soluble dietary fiber is the most effective.
Your Blood Sugar’s Relationship With Your Menstrual Cycle
How is blood sugar connected to your period?
What if you have diabetes?
How does each point in your cycle affect blood sugar?
Managing blood glucose levels alongside your cycle
In the words of Def Leppard, pour some sugar on meeeeee. Except maybe when menstruating? If you have blood sugar issues, experience hypoglycemia or suffer from diabetes, then you may have noticed fluctuations during your menstrual cycle thanks to constantly changing hormone levels. These changes can be difficult to manage in themselves, never mind the added stress of sensitivity to insulin.
If you suffer from diabetes and your hormones seem unpredictable, trying to manage your blood sugar alongside this can be challenging. One solution wont suit everyone, but here are a few things you might want to know about this frustrating but important topic…
Recommended Reading: Does Blue Cross Blue Shield Cover Testosterone Therapy
Consequences Of Blood Sugar Levels
Whilst most symptoms of low and high blood sugar levels are mild, they can worsen if left untreated and sometimes have long term consequences and/or complications. Overtime, a high blood sugar level is what can cause consequences. Lack of treatment can cause severe damage to the blood vessels and lead to complications such as:
- Heart attack
Treatment For High Blood Sugar Levels
For those with high blood sugar levels, it is vital to keep track of your blood sugars at home on a daily basis. This can be done with a glucose meter. These test monitors are often provided to diabetic patients so that they can manage their blood sugar levels at home everyday. They are available to purchase online if you are non-diabetic but wish to check on your levels regularly for safety.
Diabetic patients can be prescribed medications to help with insulin levels when their blood sugar is high. Those with type 1 diabetes will be prescribed medication which needs to be taken several times daily. This type of diabetes has no cure but can be managed with the right medication.
Those with type 2 diabetes or gestational diabetes can treat their high blood sugar with a change in diet or exercise. A healthier balanced diet is usually advised and sometimes, insulin medication is also prescribed if the blood sugar level becomes abnormally higher than the high reading for diabetic patients.
Also Check: Nugenix Estro-regulator Reviews
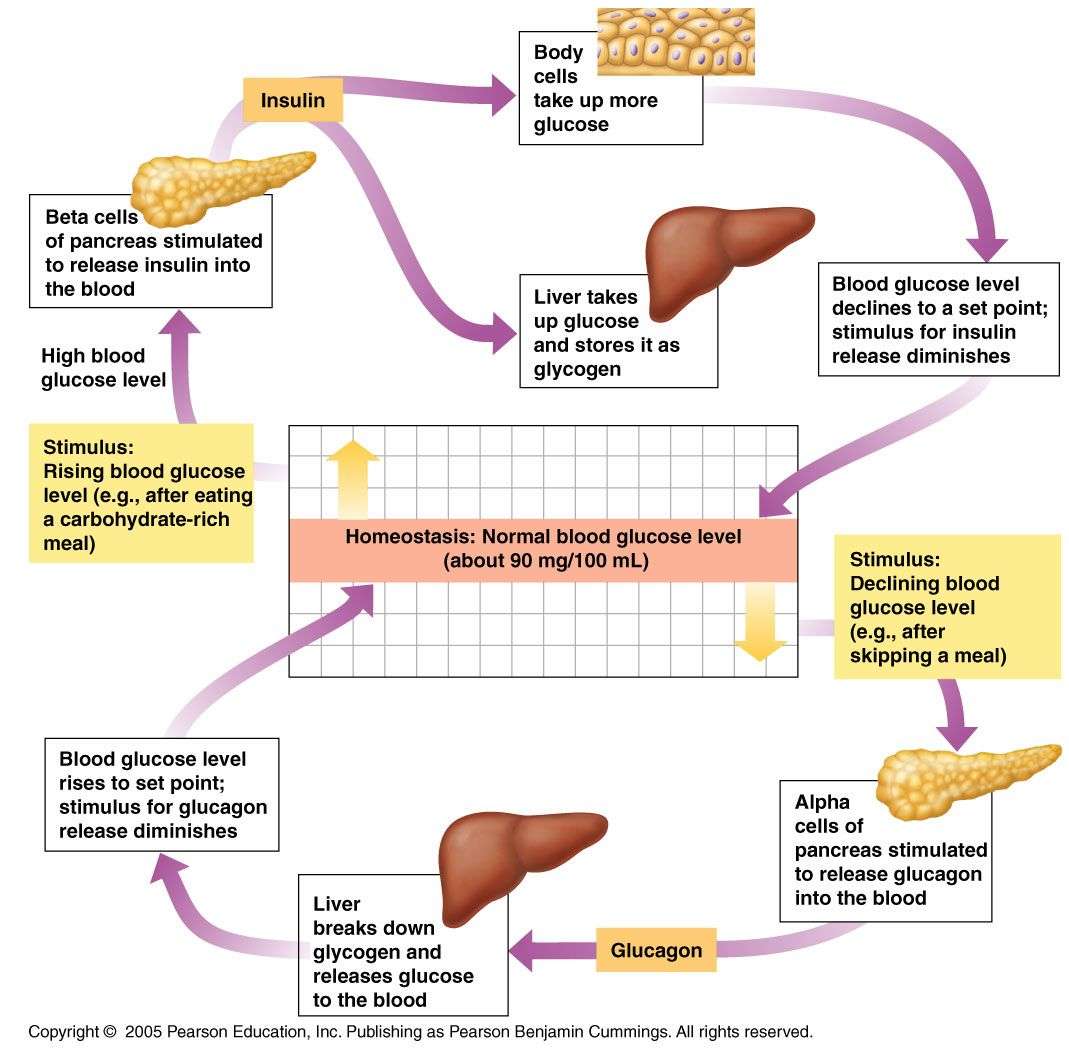
The Role Of Glucagon In Blood Glucose Control
The effect of glucagon is to make the liver release the glucose it has stored in its cells into the bloodstream, with the net effect of increasing blood glucose. Glucagon also induces the liver to make glucose out of building blocks obtained from other nutrients found in the body .
Our bodies desire blood glucose to be maintained between 70 mg/dl and 110 mg/dl . Below 70 is termed “hypoglycemia.” Above 110 can be normal if you have eaten within 2 to 3 hours. That is why your doctor wants to measure your blood glucose while you are fasting…it should be between 70 and 110. Even after you have eaten, however, your glucose should be below 180. Above 180 is termed “hyperglycemia” . If your 2 two blood sugar measurements above 200 after drinking a sugar-water drink , then you are diagnosed with diabetes.
Dawn Phenomenon And Rebound Hyperglycemia
Blood glucose levels rise sharply in the early morning due to the release of certain hormones in the middle of the night.
These counter-regulatory hormones, which include glucagon, growth hormone, epinephrine and cortisol, increase the level of blood glucose by signalling the liver to release more glucose and by hindering glucose utilisation throughout the body.
Overnight, the surge in the amount of growth hormone and cortisol released by the body effectively increases glucose production in the liver to prepare the body for activity during the day.
For individuals without diabetes, these processes are balanced out by increased insulin secretion by the pancreas, which keeps blood glucose levels relatively stable.
But in people with type 1 diabetes , whose bodies are unable to produce insulin, and type 2 diabetes , where the livers response to insulin may not be sufficient to stop glucose production, changes in glucose metabolism during sleep can have a big impact on morning blood glucose levels.
In addition to the dawn phenomenon , there is another process that can cause high blood sugar in the early hours of the day.
Also Check: Does Nugenix Have An Estrogen Blocker
Understanding The Processes Behind The Regulation Of Blood Glucose
20 April, 2004
VOL: 100, ISSUE: 16, PAGE NO: 56
Pat James, PhD, is senior lecturer in applied physiology
Roger McFadden, MSc, is senior lecturer in applied physiology both at the School of Health and Policy Studies, The University of Central England in Birmingham
Pat James, PhD, is senior lecturer in applied physiology
Glucose is one of the bodys principal fuels. It is an energy-rich monosaccharide sugar that is broken down in our cells to produce adenosine triphosphate. ATP is a small packet of chemical energy that powers the millions of biochemical reactions that take place in the body every second.
We obtain glucose from the food that we eat, predominantly starch-rich foods such as potatoes, rice, bread, and pasta. Starch is a polysaccharide that is broken down by digestive enzymes into individual glucose molecules.
In the small intestine, glucose is absorbed into the blood and travels to the liver via the hepatic portal vein. The hepatocytes absorb much of the glucose and convert it into glycogen, an insoluble polymer of glucose.
This is stored in the liver and can be reconverted into glucose when blood-glucose levels fall. Other types of simple sugars in our diet such as fructose, sucrose and lactose are also fuels that contribute to the production of ATP.
If glucose levels fall to too low a concentration or rise too high then this situation can lead to the neurological processes in the brain being compromised.
What Happens If I Have Too Little Insulin
People with diabetes have problems either making insulin, how that insulin works or both. The main two types of diabetes are type 1 and type 2 diabetes, although there are other more uncommon types.
People with type 1 diabetes produce very little or no insulin at all. This condition is caused when the beta cells that make insulin have been destroyed by antibodies , hence they are unable to produce insulin. With too little insulin, the body can no longer move glucose from the blood into the cells, causing high blood glucose levels. If the glucose level is high enough, excess glucose spills into the urine. This drags extra water into the urine causing more frequent urination and thirst. This leads to dehydration, which can cause confusion. In addition, with too little insulin, the cells cannot take in glucose for energy and other sources of energy are needed to provide this energy. This makes the body tired and can cause weight loss. If this continues, patients can become very ill. This is because the body attempts to make new energy from fat and causes acids to be produced as waste products. Ultimately, this can lead to coma and death if medical attention is not sought. People with type 1 diabetes will need to inject insulin in order to survive.
Read Also: Can Having Your Tubes Tied Cause Hormonal Imbalance
How Does Taking Prednisone Affect My Diabetes
Prednisone is used for a variety of conditions such as asthma and other lung problems. It acts like a hormone that your body makes called cortisol. Cortisol and prednisone both cause the body to make glucose when youre not eating . They can worsen diabetes control. Cortisol is called a stress hormone because the body releases it to deal with stresses like accidents, infections, or burns. Thats part of the reason why it takes more insulin to keep blood glucose near normal during an infection. If you have had prednisone prescribed for any reason and you have diabetes, you will need to take more diabetes medication. Prednisones effect on your blood glucose will go away a day or two after you stop taking it. Your health care team can help you alter your diabetes treatment until you can stop taking the prednisone.
Easy Ways To Lower Blood Sugar Levels Naturally
High blood sugar occurs when your body doesnt make enough or effectively use insulin, a hormone that regulates blood glucose and helps it enter your cells for energy.
High blood sugar is associated with diabetes.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reports that 13% of U.S. adults live with diabetes, and 34.5% have prediabetes (
This means close to 50% of all U.S. adults have diabetes or prediabetes.
Here are 15 easy ways to lower blood sugar levels naturally:
Also Check: Does Blue Cross Blue Shield Cover Testosterone Therapy
Which Side Effects Are Worse On Prednisone 20 Mg Tablets
If your doctor prescribed a prednisone 20 mg tablet or higher, then youve been given a high dose. So which prednisone side effects get worse the higher the dose? In this article, I will share the side effects to expect at higher doses of prednisone according to the five most comprehensive pharmacy databases.
My High Dose Prednisone Experience
First, I want to share my personal experience taking high doses of prednisone and other steroids. Because my immune system killed off so many of my blood platelets, doctors worried I could bleed to death. In the hospital they started with prednisone 60 mg, given as three prednisone 20 mg tablets. That only worked for a week to boost my platelets until they started to crash again.
Prednisone Failed
So the hematologist prescribed another steroid, dexamethasone. I took #10 of the highest strength dexamethasone tablets each day for three days. The dose of dexamethasone I took equals approximately 267 mg of prednisone. Eventually, that failed as well, so my doctor started me on a slow taper down from prednisone 60 mg.
Tapering Roller Coaster
They pricked my arm each week to check my platelet level and decide whether I could continue tapering or whether I needed to go back up to a higher dose. I rode that roller coaster of blood draws for six months before they eventually resorted to chemotherapy which cured my problem, at least for now. Then I finished tapering off prednisone after nine months of high-to-low doses of prednisone.
Does Hypoglycemia Cause Growth Hormone Deficiency
The relationship between growth hormone deficiency and hypoglycemia is an interesting one. Growth hormone plays an essential role in how the body metabolizes everything we eat. From protein to carbohydrates to lipids , GH helps regulate how well the food converts to the fuel we need for energy glucose. After eating, insulin secreted by the pancreas enters the bloodstream to tell the cells to take in that glucose. As insulin levels increase, growth hormone production declines.
The connection between HGH and hypoglycemia occurs when blood sugar levels decline. As the insulin promotes cellular glucose uptake, blood sugar leaves the bloodstream. Having done its job, insulin levels also decline. As a result, the hypothalamus tells the pituitary gland to make more growth hormone. With lower blood sugar levels , more growth hormone enters the bloodstream to facilitate two crucial functions lipolysis and ketogenesis. We will discuss those functions in greater detail in the next section.
The body now needs to increase blood sugar levels to avoid hypoglycemia. How does HGH cause low blood sugar to reverse? Growth hormone helps to promote the processing of glucagon stored glucose found in the liver and tissues. Once processed, the glucagon can once again enter the bloodstream as glucose.
*Blood sugar, insulin, and growth hormone are part of a delicate balance that is in a continual state of flux in the body.
Also Check: Can I Give My Cat Melatonin