Factors That May Influence Treatment Decision
The drug mechanism of action, the route of administration, the duration of treatment, the impact on quality of life and the toxicity profile are important factors to consider when selecting a therapy for a particular patient, as they are quite different among the various strategies . Docetaxel has a major incidence of myelo-suppression with potential neutropenia, fatigue and neurotoxicity. Abiraterone is associated with mineralocorticoid-associated side effects including hypertension, hypokalemia and hepatic toxicity. Enzalutamide frequently causes fatigue, hypertension and falls. Apalutamide is associated with increased risk of rash, pruritus, hot flushes, hypothyroidism and fractures. Radiotherapy to the primary tumor can cause acute and late bladder and bowel toxic effects that can remarkably affect the quality of life .
In terms of costs, docetaxel in combination with ADT is likely to be the most cost-effective treatment option for patients with mHSPC . Docetaxel is administered every 21 days for six cycles at an approximate cost of $550 per cycle, whereas novel ARSi are prescribed as a daily dosing schedule until the time of progression at an approximate cost that exceeds $7000 per month . To administer lower dosages of ARSi might be an opportunity to reduce toxicities and costs, but phase 3 non-inferiority trials are still needed .
Survival For All Stages Of Prostate Cancer
Generally for men with prostate cancer in England:
- more than 95 out of 100 will survive their cancer for 1 year or more
- more than 85 out of 100 will survive their cancer for 5 years or more
- almost 80 out of 100 will survive their cancer for 10 years or more
Survival for prostate cancer is also reported in Scotland and Northern Ireland. But it is difficult to compare survival between these countries because of differences in the way the information is collected.
Cancer survival by stage at diagnosis for England, 2019Office for National Statistics
These statistics are for net survival. Net survival estimates the number of people who survive their cancer rather than calculating the number of people diagnosed with cancer who are still alive. In other words, it is the survival of cancer patients after taking into account the background mortality that they would have experienced if they had not had cancer.
Risk Factors In Phase 3 Trials
The CHAARTED and GETUG-AFU 15 trials assessed the role of upfront docetaxel plus ADT versus ADT alone in patients with mHSPC . The prospective stratification of high-volume versus low-volume metastatic disease was introduced for the first time as an amendment to the protocol of the CHAARTED trial . Given the uncertain role of chemotherapy in low-volume disease , several subsequent trials in mHSPC have analyzed patients outcomes based on disease burden . Different from the CHAARTED trial, the LATITUDE trial of abiraterone acetate in mHSPC used another classification to define high-risk patients, which was based on the presence of two or more high risk features that included 3 bone metastases, visceral metastases and Gleason 8 . A recent meta-analysis of the aggregate data of patient subgroups from the CHAARTED and GETUG-AFU15 studies evaluated overall survival according to the metastatic tumor burden and time of metastasis occurrence . The authors identified three prognostic subgroups: good prognosis for those with prior local treatment and low-volume disease intermediate prognosis for those with prior local treatment and high-volume disease, or those with low-volume disease and de novo metastases and poor prognosis for those with de novo high-volume disease. These data were recently confirmed by a retrospective cohort of 436 consecutive patients with mHSPC treated with ADT at the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute between 1990 and 2013 .
Don’t Miss: Do Hormones Make You Gain Weight
About The 5th Annual Prostate & Urologic Cancer Symposium:
The Prostate & Urologic Cancers Symposium is held through the University of Oklahoma and the Stephenson Cancer Center to provide new insights in the treatment of prostate and urologic cancers. This single-day program consists of lectures and case discussions highlighting a multidisciplinary approach to urologic cancer care and integration of new technology in the evaluation and treatment of patients with prostate and/or urologic cancers. Dr. Cookson presented this lecture during the 5th iteration of this summit in 2019.
Please visit our collection page to view additional educational activtities from this symposium.
Also Check: Prostate Urine Risk Pur Test
Improving How Long Patients Live
The ENZAMET trialfunded in part by the drugs manufacturer, Astellas Pharma, as well as government health agencies in Canada and Australiaenrolled more than 1,100 men with hormone-sensitive metastatic prostate cancer. The men were randomly assigned to ADT combined with enzalutamide or with any of three other androgen-blocking drugs.
At a median follow-up of nearly 3 years, men who received ADT plus enzalutamide had a 33% reduced risk of death, with 80% still alive compared with 72% of men treated with ADT plus another antiandrogen drug, reported the trials lead investigator, Christopher Sweeney, M.B.B.S., of the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute.
Men in the enzalutamide group also had better clinical progression-free survival , which the research team defined as the time until the return of disease-related symptoms, the detection of new metastases on imaging scans, or the initiation of another cancer treatment for prostate cancer, whichever came first. At 3 years, 63% of men in the enzalutamide group were alive without clinical progression of their disease, compared with 33% in the standard treatment group.
Although enzalutamide appeared to be effective regardless of whether men had high- or low-volume disease, one apparent differentiating factor was planned early treatment with docetaxel. Nearly half of the men in both treatment groups received early treatment with docetaxel and, for those men, enzalutamide was not associated with longer overall survival.
Recommended Reading: What Are The Negative Effects Of Melatonin
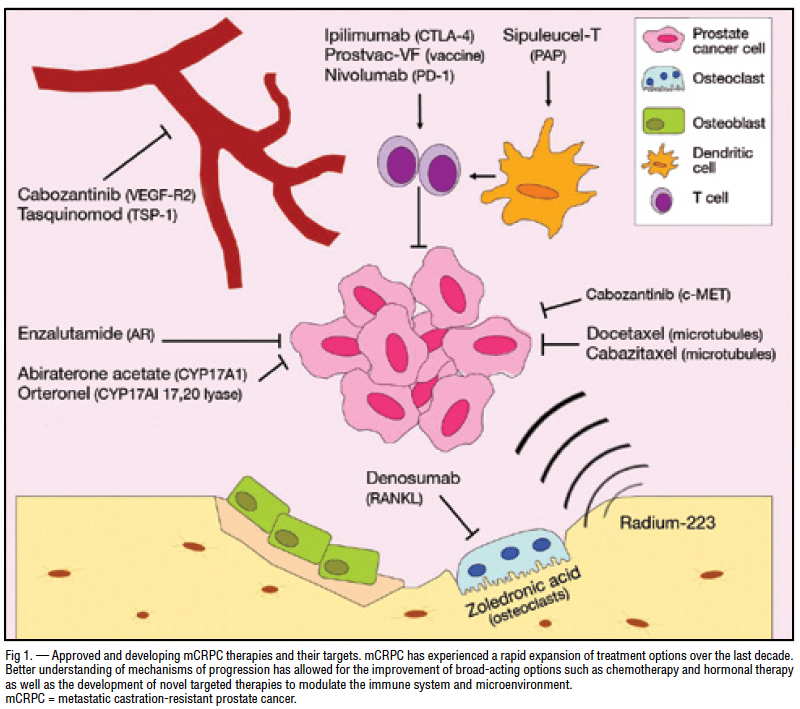
Emerging Treatments Targeting Mcrpc
Based on the above, there is a crucial need for novel alternative approaches and drugs that could overcome resistance in advanced PCa stages. In fact, several treatments, which are under development and trials, could emerge as promising therapies for patients with mCRPC and become the next-generation standards of care. Table 2 summarizes the evolving targeted treatments in mCRPC along with their relevant clinical trials.
| Ongoing trial interim results show that Ipat prolonged PFSTwo treatment-related deaths occurred in both groups |
ABI: Abiraterone ADC: antibody-drug conjugate AEs: adverse events CAR-T cells: chimeric antigen receptor T cells DDR: DNA-damage repair DOC: docetaxel ENZ: enzalutamide IgG1: immunoglobulin G1 Ipat: ipatasertib LuPSMA: lutetium-177-PSMA-617 MMAE: monomethyl auristatin E OS: overall survival PARPi: poly polymerase inhibitor PFS: progression-free survival PSA: prostate-specific antigen PSA50: > 50% decline in prostate-specific antigen PSMA: prostate-specific membrane antigen RR: response rate TGF: transforming growth factor-.
Does Crpc Affect Different Ethnic/racial Groups Differently
Non-Hispanic Black people are much more likely to get prostate cancer than those of any other race or ethnicity. Prostate cancer rates are lowest among non-Hispanic Asian Americans. Black people also are more likely than non-Black people to be diagnosed with advanced prostate cancer. But in treatment, Black people have at least similar outcomes compared to non-Black people. Researchers donât fully understand the reasons for these differences.
Show Sources
You May Like: Can Dermatologist Treat Hormonal Acne
Risk Of Bias Assessment
Two investigators independently assessed risk of bias using predefined criteria. Disagreements were resolved by consensus. For randomized trials and cohort studies, methodologists adapted criteria for assessing risk of bias from the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. Criteria for randomized trials included use of appropriate randomization and allocation concealment methods, baseline comparability of groups, blinding, attrition, and use of intention-to-treat analysis. For cohort studies on prognostic factors, criteria included methods for assembling cohorts, attrition, blinding assessment of outcomes, and adjustment for potential confounding.
The methodology team assessed systematic reviews using AMSTAR 2 criteria. Criteria included use of pre-specified methods, appropriate search methods, assessment of risk of bias, and appropriate synthesis methods. Studies were rated as âlow risk of bias,ââmedium risk of bias,â or âhigh risk of biasâ based on the presence and seriousness of methodological shortcomings.
Studies rated âlow risk of biasâ are generally considered valid. âLow risk of biasâ randomized trials include clear descriptions of the population, setting, interventions, and comparison groups a valid method for allocation of patients to treatment low dropout rates and clear reporting of dropouts blinding of patients, care providers, and outcome assessors and appropriate analysis of outcomes.
Other New Approaches In Mcrpc
Other drugs in clinical trials for mCRPC do not rely on the presence of defined mutations. Here, I discuss only those that already have promising preliminary results:
Most prostate cancer cells express a protein called PSMA on their surface. In fact, PSMA is almost exclusively found on prostate cancer cells, making it a good therapeutic target. The novel drug 177Lu-PSMA-617 is a radioactive molecule attached to another molecule that specifically targets cells expressing PSMA. The most recent results from a randomized clinical trial where men received either LuPSMA or the chemotherapy drug cabazitaxel show that response rate was higher with LuPSMA than with cabazitaxel.
Currently, there are two other radionuclide conjugates that target PSMA in trials: BAY 2315497 and 225AcJ591.
PSMA can also be targeted by other means, one of which is a very interesting approach known as CAR T-cell treatment, currently available in two trials. CAR T-cell treatment is beneficial in liquid tumors of the blood or bone marrow, but has yet to be validated in solid tumors like prostate cancer. However, some results are promising. The presence of a good target for these engineered cancer-killing immune cells is a good omen in prostate cancer, because identifying specific targets in solid tumors is a major hurdle in designing CAR T-cell treatments.
Read Also: How To Remove Hormonal Belly Fat
Bone Pain In Prostate Cancer
Many advanced prostate cancer patients often suffer from bone pain that adversely affect quality of life. The management of pain or other cancer related functional impairment is integral part of palliative care. Palliative management can include analgesics, glucocorticoids, palliative chemotherapy, radioisotopes or radiotherapy.
Radioisotopes that selectively concentrate in bone lesions are approved for the palliative treatment of painful bone metastases. The treatment is of more value in patients with multiple metastases . The radioisotopes have been found to reduce the need for opioid painkillers in such patients.
EBRT is effective in painful bone lesions in advanced prostate cancer patients but not an ideal option if there are multiple lesions at different sites. The lesions in multiple sites will progress after EBRT in one site and pain will reappear in a short time afterwards, unless other systemic therapies are initiated to control the disease process. Read more on EBRT under prostate cancer treatments.
Dont Miss:
Selection Of Therapy For Crpc
With the range of newer treatment options becoming available, it is clear there will be a need to more carefully define the most appropriate treatment for individual patients with CRPC. As the incidence of prostate cancer is disproportionately high in elderly men, consideration should be given to life expectancy issues, functional status, and the ability of a patient to tolerate potential side effects of therapies . Because elderly patients also may benefit from chemotherapies to the same degree that younger patients do, we should ensure that all treatment options that prolong survival, control symptoms, reduce pain, and improve quality of life are available to those patients with good clinical status. Strategies such as proteomic profiling have been used to define markers that predict docetaxel resistance in men with mCRPC, and use of such biomarkers potentially could better define which patients will experience recurrence early on docetaxel therapy and direct these patients to a more appropriate therapy . Other surrogate biomarkers for prediction of clinical benefit in mCRPC include PSA, bone turnover markers, bone pain, bone scans, and circulating tumor cells . The use of these surrogate biomarkers has the potential to improve patient selection strategies, and more rapidly identify agents that merit further testing in phase 3 clinical trials, as well as accelerate phase 3 testing. However, these markers will require validation for use in patients with mCRPC .
Read Also: Can You Cure Hormonal Acne
When Is Hormone Therapy Used
Hormone therapy may be used:
- If the cancer has spread too far to be cured by surgery or radiation, or if you cant have these treatments for some other reason
- If the cancer remains or comes back after treatment with surgery or radiation therapy
- Along with radiation therapy as the initial treatment, if you are at higher risk of the cancer coming back after treatment
- Before radiation to try to shrink the cancer to make treatment more effective
Hormonal Therapy And Chemotherapy In Metastatic Disease
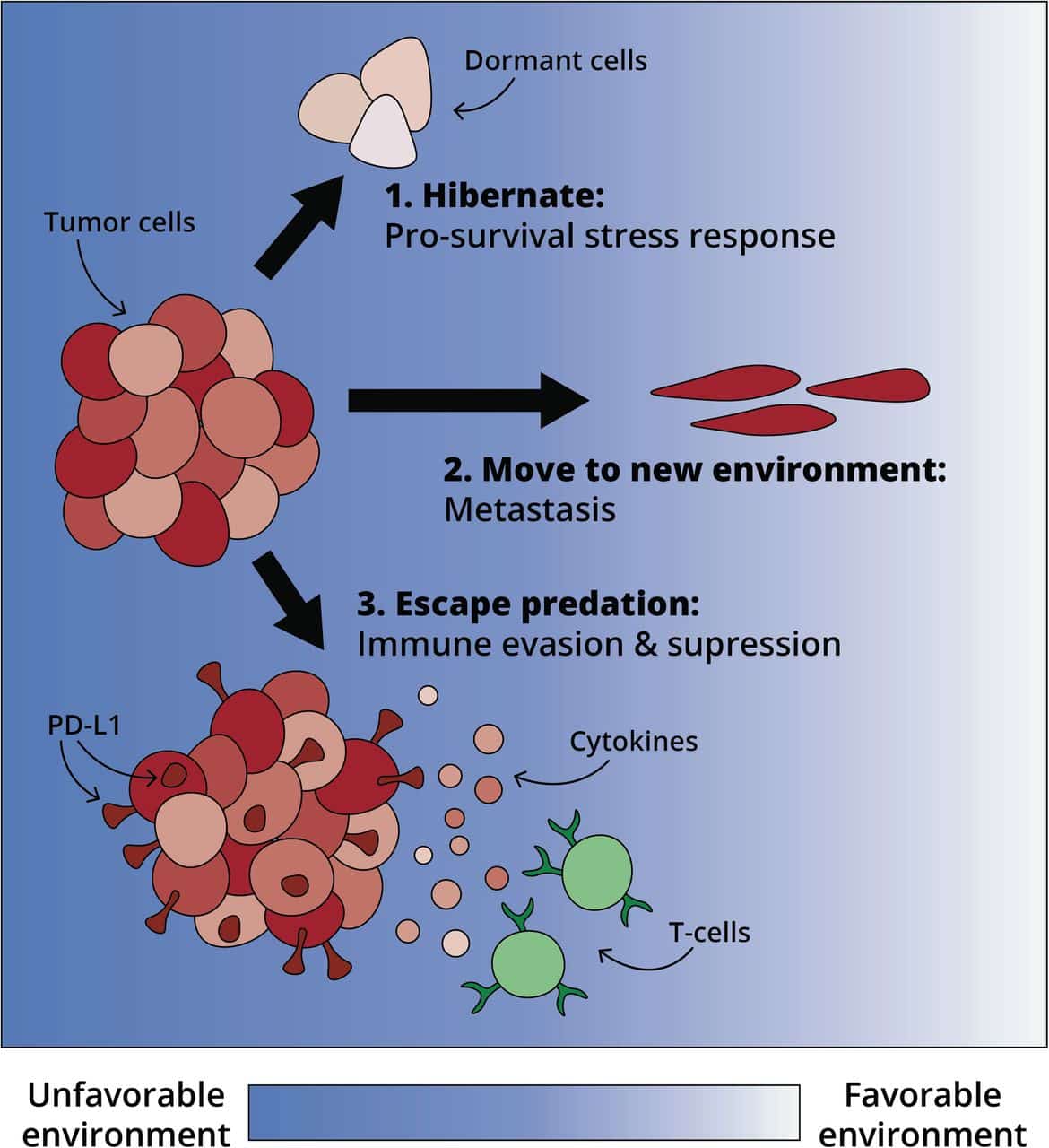
It has been recently demonstrated that the use of chemotherapy can improve outcomes in patients with metastatic hormone naive prostate cancer. It appears that some patients initiating hormonal therapy may actually be better candidates for cytotoxic therapy at this stage of disease than when their disease becomes castration resistant .
It has been controversial as to whether or not early chemotherapy in hormone naive patients would be beneficial. There have been arguments for and against this approach. In favor is the idea that attacking de novo testosterone independent clones early should allow ADT to keep prostate cancer in remission longer. In addition, there is the possibility that some patients at the time of progression may be too frail to receive chemotherapy.
Alternatively, ADT may take cells out of cycle and make them less responsive to cytotoxics. The fact that some patients respond for long periods to ADT and never need chemotherapy is the other argument against early chemotherapy.
Since the early 80s several studies tried to clarify these differing viewpoints, investigating the addition of chemotherapy with hormonal therapy in patients with metastatic prostate cancer .
None of the trials reported positive results, concluding that androgen suppression remains the preferred first line treatment in metastatic prostate cancer and that there was no cytotoxic regimen with consistent activity against hormone-sensitive prostate cancer.
Recommended Reading: Does Medicare Pay For Testosterone Injections
Pharmacologic Agents In Prostate Cancer
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone analogues suppress ovarian and testicular steroidogenesis by decreasing luteinizing hormone and follicle stimulating hormone levels, whereas GnRH antagonists lower serum testosterone levels by suppressing LH and FSH.
Bisphosphonates are analogues of pyrophosphate that act by binding to hydroxyapatite in bone matrix, thereby inhibiting the dissolution of crystals. These agents prevent osteoclast attachment to the bone matrix and osteoclast recruitment and viability.
Antiandrogens are used as combination agents to treat prostate cancer. Antifungal agents produce a response similar to that of antiandrogens. These drugs inhibit various cytochrome P-450 enzymes, including 11-beta-hydroxylase and 17-alpha-hydroxylase, which in turn inhibit steroid synthesis. The antiandrogen abiraterone is a 17 alpha-hydroxylase/C17, 20-lyase inhibitor that was approved by the US Food and Drug Administration in 2011 for use in combination with prednisone for treatment of metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer in patients who received prior chemotherapy containing docetaxel.
An ultramicronized abiraterone tablet was approved in May 2018 for CRPC in combination with methylprednisolone. The ultramicronized formulation may be administered with or without food, whereas, the original tablet formulation must be administered 1 hour before or 2 hours after meals.
Hormonal Therapy And Chemotherapy In Crpc Patients
CRPC is an aggressive disease that contains heterogeneous types of cells developing a variety of abnormal pathways to survive in a castrate environment. The biological heterogeneity of prostate cancer cells has become clear as there are different clinical subsets of patients, from indolent tumors to those that are aggressive and lethal with multiple metastases. The biological and clinical heterogeneity dictates the different therapeutic options in the management of CRPC.
You May Like: Does Tricare Cover Testosterone Therapy
How Long Can Someone Live With Stage 4 Cancer
Doctors usually describe a persons outlook using the 5-year survival rate. These are calculated based on data from thousands of other people with a similar cancer at a similar stage.
The original location of the cancer determines its type. Survival rates vary, depending on the type of cancer and how far it has spread within the body.
Below, we describe the survival rates for some of the most common forms of cancer in stage 4:
The Pi3k/akt/mammalian Target Of Rapamycin Pathway
The PI3K pathway is one of the most critical in human cancer. Various growth factors, including insulin-like growth factor and fibroblast growth factor , regulate this pathway, leading to activation of PI3K and the formation of PIP3. PIP3 activates AKT via phosphorylation and phosphorylated Akt activates multiple molecules involved in cell survival and proliferation, including MDM2, c-myc, GSK3, nuclear factor-B and mTOR. Phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted on chromosome 10 is a lipid phosphatase that functions as the main inhibitor of PI3K/Akt signaling. Genetic alterations of the PI3K signaling pathway occur in 42% and 100% of primary and metastatic prostate cancers, respectively, suggesting this pathway is crucial in the development of CRPC.
Additional experiments showed that after 7 days of enzalutamide treatment of Ptenloxp/loxp mice, despite decreased AR transcriptional activity the tumors had not significantly regressed and were histologically similar to those before treatment, although the treatment was much more effective in transgenic mice with inducible c-myc. Further studies revealed increased Akt phosphorylation at Ser473 in the Ptenloxp/loxp mice and in LNCaP and LAPC4 AR-positive cells after castration and enzalutamide treatment, respectively. The same treatment did not increase pAkt in PC-3 cells, which are AR negative.
Also Check: How To Test Your Estrogen Levels At Home
Tailoring Treatment Aims To The Individual Goal
As alluded to earlier in the review, treatment of the mHSPC patient must take into context the overriding individual treatment aim. For most patients, metastatic prostate cancer is an incurable disease. The aim is to transform mHSPC into a manageable chronic illness so that the patient dies with the cancer, rather than of it.
For the young patient with few comorbidities presenting with mHSPC, the risk of dying from metastatic prostate cancer is significant. The likely treatment aim is to prolong OS with respect to the cancer. In the absence of a clearly superior agent and prospective sequencing data, the strategy is to maximise the lines of therapies that can be utilized in the patients treatment course. The reasoning of the treating oncologist may be to administer docetaxel in the upfront setting, taking into account that the more tolerable oral antiandrogens can be added on more easily than docetaxel at a later point should the patient become increasingly frail from the disease and/or other underlying comorbidities.