What Are The Side Effects Of Hormone Therapy
The side effects of hormone therapy depend largely on the specific drug or the type of treatment . The benefits and harms of taking hormone therapy should be carefully weighed for each person. A common switching strategy used for adjuvant therapy, in which patients take tamoxifen for 2 or 3 years, followed by an aromatase inhibitor for 2 or 3 years, may yield the best balance of benefits and harms of these two types of hormone therapy .
Hot flashes, night sweats, and vaginal dryness are common side effects of all hormone therapies. Hormone therapy also may disrupt the menstrual cycle in premenopausal women.
Less common but serious side effects of hormone therapy drugs are listed below.
Tamoxifen
- breathing problems, including painful breathing, shortness of breath, and cough
- loss of appetite
Types Of Hormone Therapy For Ovarian Cancer
There are different types of ovarian cancer hormone therapy drugs, including:
Luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone agonists. These drugs curb estrogen production in your ovariesâ cells. You might take them if you arenât in menopause.
You get these drugs as shots at your treatment center or doctorâs office. Your doctor may choose to give it to you every 1 to 3 months, depending on the stage and type of cancer you have. LHRH agonist drugs used for ovarian cancer include:
Tamoxifen. You may know of tamoxifen as a breast cancer treatment. It can also be used to treat ovarian stromal tumors, and itâs less likely to be used to treat ovarian epithelial cancer. Tamoxifen works to keep estrogen in your body from helping your cancer grow and spread.
If tamoxifen is part of your treatment plan, youâll get regular tests to check on whether it is working properly and manage any side effects you may have. You shouldnât take tamoxifen if you also take a blood thinner medication such as warfarin.
Research shows that tamoxifen can also raise your risk for other types of cancers like those of the liver, uterus, or endometrium. It can also make blood clots more likely, which can cause serious conditions like deep vein thrombosis . If youâre taking tamoxifen and notice any swelling or pain in your legs, arms, chest, or shortness of breath, tell you doctor right away. If you have a DVT, youâll need immediate treatment.
Aromatase inhibitors include:
Treatment For Ovarian Cancer
Treatment for ovarian cancer will depend on:
- the size and type of ovarian cancer you have
- where the cancer is
The main treatments are surgery and chemotherapy. Other treatments include targeted medicines and hormone treatments.
The specialist care team looking after you will:
- explain the treatments, benefits and side effects
- work with you to create a treatment plan that is best for you
- talk to you about how treatment may affect you, for instance if there are any side effects
You’ll have regular check-ups during and after any treatments. You may also have tests and scans.
If you have any symptoms or side effects that you are worried about, talk to your specialists. You do not need to wait for your next check-up.
Recommended Reading: Is The Skyla Iud Hormonal
Ovarian Cancer Treatment By Stage
Treatment for ovarian cancer typically starts with surgery to remove the tumors and check for cancer in the lymph nodes. The extent of the surgery will depend on the cancers stage. Additional treatment with chemotherapy and/or targeted therapy, such as PARP inhibitors or monoclonal antibodies, are also options that will depend on the stage of the cancer.
Stage 2 Stage 3 And Stage 4 Ovarian Cancer Treatment
If surgery reveals that cancer has spread to the lymph nodes or other structures in the abdomen, doctors classify it as more advanced. For stages 2, 3 and 4 ovarian cancers, the care team may recommend other treatments along with surgery.
Depending on the tumor size, doctors may recommend chemotherapy or targeted therapy before surgery to shrink the tumor. This approach is called neoadjuvant therapy.
Surgery may be followed by chemotherapy , targeted therapy or both.
More specifically:
- Stage 2 ovarian cancer treatment is often surgery followed by chemotherapy.
- Stage 3 ovarian cancer treatment usually involves more extensive surgery, which will remove the reproductive organs and other structures such as the fatty tissue around the stomach and intestines. This is typically followed by several rounds of chemotherapy and targeted therapy. Patients may continue on targeted therapy for a year after chemotherapy ends.
- Stage 4 ovarian cancer treatment may begin with chemotherapy before surgery and then follow the treatment plan used for stage 3 ovarian cancer. Sometimes combination targeted therapies are recommended. Depending on the stage of the cancer, palliative procedures and medicines may be used to help reduce fluid buildup or blockages and help extend the patients life.
Don’t Miss: Eating To Balance Your Hormones
Hormonal Therapy For Ovarian Cancer
Hormonal therapy is sometimes used to treat ovarian cancer. It is a treatment that adds, blocks or removes hormones. Hormones are substances that control some body functions, including how cells act and grow. Changing the levels of hormones or blocking certain hormones can slow the growth and spread of ovarian cancer cells. Drugs, surgery or radiation therapy can be used to change hormone levels or block their effects.
You may have hormonal therapy to:
- treat some types of ovarian cancer when they are advanced or have recurred
- control cancer cells left behind after surgery
Your healthcare team will consider your personal needs to plan your hormonal therapy. You may also receive other treatments.
Who Is A Candidate For Hrt
When deciding whether to use HRT, you should consider the possible positive and negative effects. HRT may be worthwhile for people with moderate or severe hot flashes as well as those who have gone into menopause early. It can also be an option for women who are experiencing bone loss when other bone-strengthening treatments arent working.
HRT may not be a good option for those who are older than 60 years old and those who began going through the menopause cycle more than 10 years ago. People who have a family history or personal risk of blood clots, stroke, liver disease, or cancer may also want to avoid HRT.
If you are concerned about your chances of developing ovarian cancer, talk to your health care team about whether HRT is right for you. If you choose not to use HRT, other treatments may be available.
Different prescription medications that do not contain hormones can help treat various menopausal symptoms. Additionally, symptoms tend to be milder if you avoid caffeine and alcohol, or manage stress levels through meditation or other relaxation exercises.
Don’t Miss: How To Increase Your Estrogen Levels Naturally
Hormone Therapy Drugs For Ovarian Cancer
If hormone therapy is part of your ovarian cancer treatment, youâll likely also get other treatments like chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or surgery.
The type of drug your doctor will include in your treatment plan will depend on:
- The type of ovarian cancer you have
- The size of the tumor in your ovaries
- If hormone receptors are present on cancer cells
How To Tell If Hormone Therapy Is Working
If you are taking hormone therapy for prostate cancer, you will have regular PSA tests. If hormone therapy is working, your PSA levels will stay the same or may even go down. But, if your PSA levels go up, this may be a sign that the treatment is no longer working. If this happens, your doctor will discuss treatment options with you.
If you are taking hormone therapy for breast cancer, you will have regular check-ups. Checkups usually include an exam of the neck, underarm, chest, and breast areas. You will have regular mammograms, though you probably wont need a mammogram of a reconstructed breast. Your doctor may also order otherimaging procedures or lab tests.
Don’t Miss: Does Hormone Therapy Work For Weight Loss
Hormone Therapy And Breast Cancer
Previous research has shown an association between hormone replacement therapy and an increased risk for breast cancer. A study published last month in The Journal of the American Medical Association found that postmenopausal women who take a combination of estrogen and progestin therapy face a greater risk for developing a more advanced form of breast cancer and an increased risk for dying from the disease. The findings were based on the ongoing Womenâs Health Initiative, a major research program launched in 1991 by the National Institutes of Health.
In the United States, ovarian cancer is the fifth leading cause of cancer death. According to 2006 data from the CDC, 19,994 women in the U.S. were diagnosed with ovarian cancer and 14,857 women died from the disease.
Show Sources
Ninth Annual American Association for Cancer Research Frontiers in Cancer Prevention Research Conference, Philadelphia, Nov. 7-10, 2010.
Chlebowski, R. TheJournal of the American Medical Association, Oct. 20, 2010 vol 304: pp 1684-1692.
CDC.
Hormone Therapy And Risk For Ovarian Cancer
Investigators led by Konstantinos Tsilidis, PhD, looked at data on 126,920 postmenopausal women who did not have a history of cancer and who had not had their ovaries removed. During nine years of follow-up, there were 424 cases of ovarian cancer diagnosed.
The women were also asked about their height and weight, whether they smoked, use of oral contraceptives, number of pregnancies, and what age they started menstruating.
After accounting for other factors, the research team found that:
- 45% of the group had used hormone therapy at some point.
- 30% were current users of hormone therapy when the study started.
- 69% of the group that used hormone therapy took an estrogen-progestin combination, 18% used estrogen-only hormone therapy, 3% used tibolone, and 2% used other preparations of hormone therapy 8% had missing information on type of hormone use.
- Current use of any hormone therapy was significantly associated with a 29% increased risk of ovarian cancer compared to women who had never used hormone therapy.
- Current use of estrogen-only therapy was associated with a 63% increased risk of ovarian cancer.
- Current use of estrogen-progestin combination therapy was not significantly associated with risk.
- Women who had ever used some form of hormone therapy for five or more years had a 45% higher risk for ovarian cancer compared with women who had never used hormone therapy.
Read Also: Female Birth Control Non Hormonal
Hormone Replacement In Premenopausal Women Treated With Bilateral Oophorectomy For Ovarian Cancer A Nationwide Population
- AffiliationsDepartment of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Danderyd Hospital, Stockholm, SwedenDepartment of Women’s and Children’s Health, Division of Neonatology, Obstetrics and Gynecology, Karolinska Institute, Stockholm, Sweden
- Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Sahlgrenska University Hospital, Gothenburg, SwedenInstitute of Clinical Sciences, Sahlgrenska Academy at University of Gothenburg, Gothenburg, Sweden
- Department of Reproductive Medicine, Division of Gynecology and Reproduction, Karolinska University Hospital, SwedenDepartment of Oncology-Pathology, Karolinska Institute, Stockholm, Sweden
- Department of Oncology, Institute of Clinical Sciences, Sahlgrenska Academy, University of Gothenburg, SwedenRegional Cancer Centre Western Sweden, Sahlgrenska University Hospital, Gothenburg, Sweden
- Angelique Flöter RådestadAffiliationsDepartment of Women’s and Children’s Health, Division of Neonatology, Obstetrics and Gynecology, Karolinska Institute, Stockholm, SwedenDepartment of Hereditary Cancer, Karolinska University Hospital, Stockholm, Sweden
- HRT prescription pick-up is low in women with premature menopause and ovarian cancer.
- < 50% of premenopausal women with ovarian cancer were dispensed HRT after surgical menopause.
- Young age and borderline ovarian tumors were factors that led to a significant dispensing of HRT.
Clinical Impact Of Ovarian Cancer
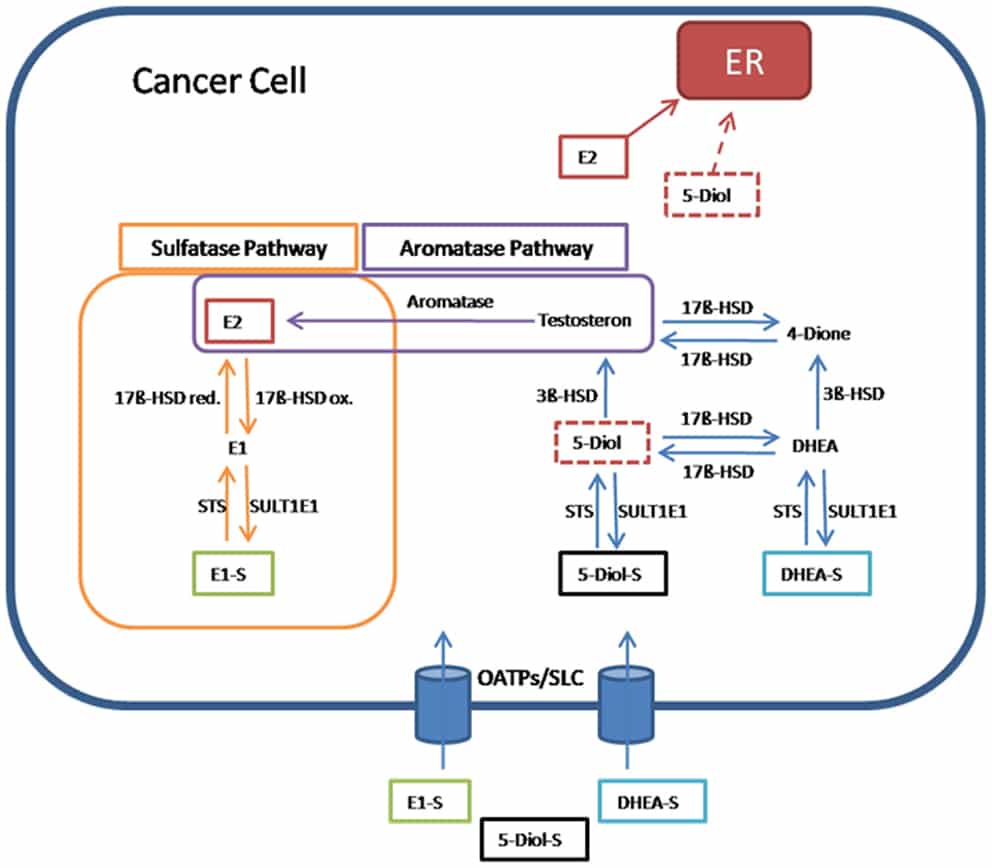
Ovarian cancer is the most lethal gynecological cancer in the United States and the fourth leading cause of cancer death in women. In 2011, approximately 21,990 women were diagnosed and over 15,000 women died from ovarian cancer . Above 70% of women are diagnosed with late stage III and IV disease . Despite aggressive surgery to remove the bulk of the tumor at diagnosis and post-surgical treatment with platinum/ taxane-based chemotherapy, about 70% of ovarian cancers relapse within 2 years . Recurrent disease has a poor prognosis, with a 5 year survival of 23% and 14% for stage III and IV disease, respectively . Survival has minimally improved over the past decade for advanced stages and clearly new therapies are needed. The goals of salvage therapy are to palliate symptoms and to maximize quality of life. A less toxic regimen, such as hormonal therapy, is particularly appealing in this setting. Thus, convenient regimens that have clinical benefit with minimal toxicity are essential for this population.
Recommended Reading: How Can I Balance My Hormones To Stop Acne
Reducing Ovarian Cancer Risk While On Hrt
Certain strategies can help people minimize risk of developing health conditions while using HRT medications. Taking the lowest possible dose that still provides symptom relief can help. Additionally, when you stop using HRT as soon as possible after your menopausal symptoms disappear, you lessen your risk.
If you experience vaginal or urinary problems, but dont have other symptoms like hot flashes, it may be a good idea to use a vaginal insert form of HRT rather than systemic medications, like pills that are taken orally. This is because the vaginal insert forms usually contain lower doses of hormones than systemic options. It is also because hormones delivered systemically are usually absorbed into the bloodstream, where they can affect other organs in the body
Adopting healthy lifestyle habits may also help protect against cancer. While they dont seem to lower a persons overall risk of ovarian cancer, practicing more of these habits may be linked to a smaller likelihood of developing certain types of ovarian cancer, including serous cancer and metastatic cancer .
Healthy habits include:
- Eating a balanced diet full of nutrients
- Getting more physical activity
Hormone Therapy Linked To Ovarian Cancer
Estrogen-Only Therapy More Strongly Associated With Greater Risk for Ovarian Cancer
Nov. 9, 2010 — Postmenopausal women who use hormone replacement therapy face a 29% increased risk of ovarian cancer, according to a study.
Researchers at the Cancer Epidemiology Unit at the University of Oxford in England analyzed data from the European Prospective Investigation Into Cancer and Nutrition to evaluate the relationship between hormone therapy use during the postmenopausal years and ovarian cancer risk.
Also Check: Does Hormone Therapy For Breast Cancer Cause Hair Loss
How Hormone Therapy Is Used Against Cancer
Hormone therapy is used for two main reasons.
- Treat cancer. Hormone therapy can stop or slow cancer’s growth and reduce the chance it will return.
- Ease cancer symptoms. Hormone therapy may be used to reduce or prevent symptoms in men with prostate cancer who are not able to have surgery or radiation therapy.
Description Of The Condition
One in 70 women will develop ovarian cancer and its agestandardized incidence rate is 6.6 per 100,000 women . This is lower in Western Africa and higher in Northern Europe, varying from 3 to 13 per 100,000) . One in 100 women will die of the disease and the ASR of mortality is 3.9 per 100,000 . The median age at diagnosis of epithelial ovarian cancer is 60 years . However, 40% of women affected are 30 to 60 years old and 3% to 17% are less than 40 years old . The majority of women with EOC have advanced stage disease at presentation and the overall fiveyear survival for all stages is 45% .
Studies have demonstrated that the origin of many highgrade serous EOCs , the most common histological subtype of EOC, may be the fimbrial end of the fallopian tube . In this review, we use the terms ‘EOC’ and ‘ovarian cancer’ as umbrella terms to include primary peritoneal and fallopian tube HG serous cancers.
Don’t Miss: Where Can You Get Estrogen
Can Other Drugs Interfere With Hormone Therapy
Certain drugs, including several commonly prescribed antidepressants , inhibit an enzyme called CYP2D6. This enzyme plays a critical role in the body’s use of tamoxifen because CYP2D6 metabolizes, or breaks down, tamoxifen into molecules, or metabolites, that are much more active than tamoxifen itself.
The possibility that SSRIs might, by inhibiting CYP2D6, slow the metabolism of tamoxifen and reduce its effectiveness is a concern given that as many as one-fourth of breast cancer patients experience clinical depression and may be treated with SSRIs. In addition, SSRIs are sometimes used to treat hot flashes caused by hormone therapy.
Many experts suggest that patients who are taking antidepressants along with tamoxifen should discuss treatment options with their doctors, such as switching from an SSRI that is a potent inhibitor of CYP2D6, such as paroxetine hydrochloride , to one that is a weaker inhibitor, such as sertraline or citalopram , or to an antidepressant that does not inhibit CYP2D6, such as venlafaxine . Or doctors may suggest that their postmenopausal patients take an aromatase inhibitor instead of tamoxifen.
Other medications that inhibit CYP2D6 include the following:
- quinidine, which is used to treat abnormal heart rhythms
Menopausal Hormone Replacement Therapy And The Risk Of Ovarian Cancer: A Meta
- 1Department of Reproductive, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University, Kunming, China
- 2Department of Gynecology, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University, Kunming, China
- 3Department of Surgery, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University, Kunming, China
- 4Department of Oncology, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University, Kunming, China
Background: Findings by epidemiologic studies on menopausal hormone replacement therapy and the risk of ovarian cancer are inconsistent. This study aimed to assess the association of menopausal HRT with the risk of ovarian cancer by histological subtype.
Methods: A literature search was performed in PubMed, Web of Science, and EmBase for relevant articles published from inception to August 2018. Pooled relative risk ratios with 95% confidence intervals were determined with a random-effects model.
This meta-analysis suggests that menopausal HRT may increase the risk of ovarian cancer, especially for serous and endometrioid tumors.
Read Also: Restore Hormonal Vitality And Wellness Center