How Does Hormone Therapy Work Against Prostate Cancer
Early in their development, prostate cancers need androgens to grow. Hormone therapies, which are treatments that decrease androgen levels or block androgen action, can inhibit the growth of such prostate cancers, which are therefore called castration sensitive, androgen dependent, or androgen sensitive.
Most prostate cancers eventually stop responding to hormone therapy and become castration resistant. That is, they continue to grow even when androgen levels in the body are extremely low or undetectable. In the past, these tumors were also called hormone resistant, androgen independent, or hormone refractory however, these terms are rarely used now because the tumors are not truly independent of androgens for their growth. In fact, some newer hormone therapies have become available that can be used to treat tumors that have become castration resistant.
Active Surveillance And Watchful Waiting
If prostate cancer is in an early stage, is growing slowly, and treating the cancer would cause more problems than the disease itself, a doctor may recommend active surveillance or watchful waiting.
Active surveillance. Prostate cancer treatments may seriously affect a personâs quality of life. These treatments can cause side effects, such as erectile dysfunction, which is when someone is unable to get and maintain an erection, and incontinence, which is when a person cannot control their urine flow or bowel function. In addition, many prostate cancers grow slowly and cause no symptoms or problems. For this reason, many people may consider delaying cancer treatment rather than starting treatment right away. This is called active surveillance. During active surveillance, the cancer is closely monitored for signs that it is worsening. If the cancer is found to be worsening, treatment will begin.
ASCO encourages the following testing schedule for active surveillance:
-
A PSA test every 3 to 6 months
-
A DRE at least once every year
-
Another prostate biopsy within 6 to 12 months, then a biopsy at least every 2 to 5 years
Treatment should begin if the results of the tests done during active surveillance show signs of the cancer becoming more aggressive or spreading, if the cancer causes pain, or if the cancer blocks the urinary tract.
Also Check: 10 Early Warning Signs Of Prostate Cancer
Relevance Of Trial Data In Real
After decades without significant progress in the treatment landscape of mHSPC, the results of the above-mentioned trials are welcome. Nevertheless, we need to cautiously interpret these results, taking into consideration the between-study heterogeneity in study populations, and how well they reflect our patient population .
Don’t Miss: How To Relieve Stress Hormones
Tailoring Treatment Aims To The Individual Goal
As alluded to earlier in the review, treatment of the mHSPC patient must take into context the overriding individual treatment aim. For most patients, metastatic prostate cancer is an incurable disease. The aim is to transform mHSPC into a manageable chronic illness so that the patient dies with the cancer, rather than of it.
For the young patient with few comorbidities presenting with mHSPC, the risk of dying from metastatic prostate cancer is significant. The likely treatment aim is to prolong OS with respect to the cancer. In the absence of a clearly superior agent and prospective sequencing data, the strategy is to maximise the lines of therapies that can be utilized in the patients treatment course. The reasoning of the treating oncologist may be to administer docetaxel in the upfront setting, taking into account that the more tolerable oral antiandrogens can be added on more easily than docetaxel at a later point should the patient become increasingly frail from the disease and/or other underlying comorbidities.
What Is Intermittent Adt
Researchers have investigated whether a technique called intermittent androgen deprivation can delay the development of hormone resistance. With intermittent androgen deprivation, hormone therapy is given in cycles with breaks between drug administrations, rather than continuously. An additional potential benefit of this approach is that the temporary break from the side effects of hormone therapy may improve a mans quality of life.
Randomized clinical trials have shown similar overall survival with continuous ADT or intermittent ADT among men with metastatic or recurrent prostate cancer, with a reduction in some side effects for intermittent ADT .
You May Like: How Much Does Testosterone Cream Cost
Definitive Treatment Is Beneficial Only In Patients With Low
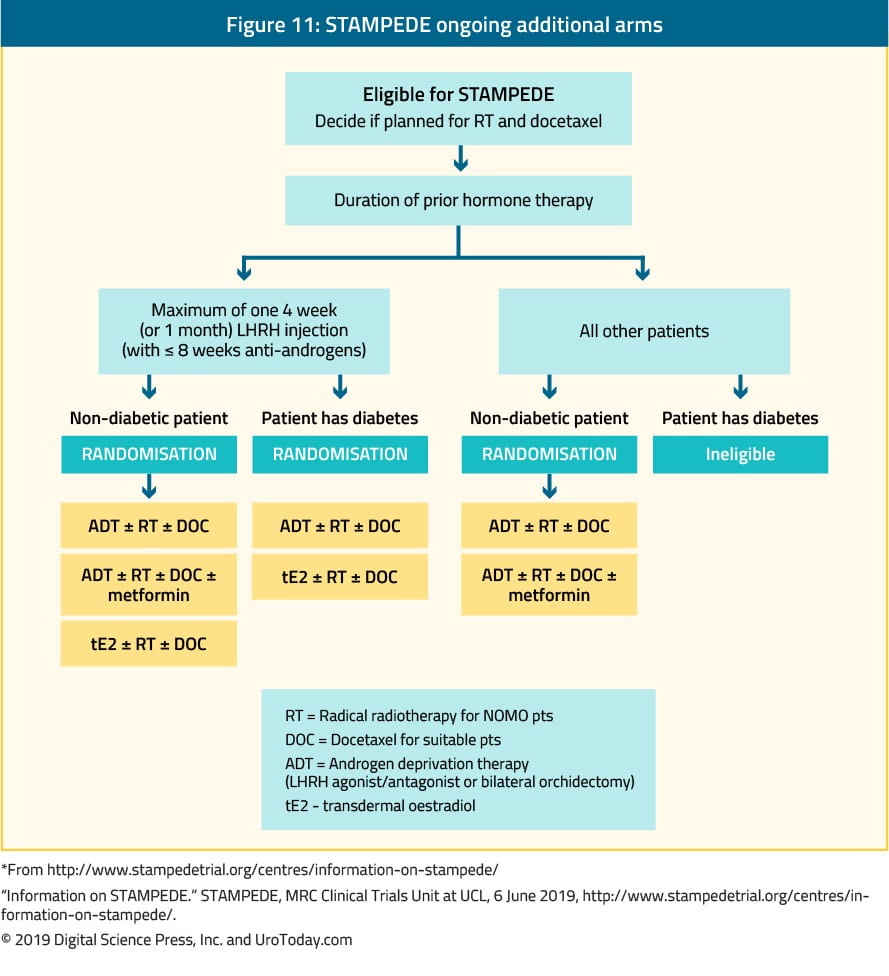
Not only systemic pharmacotherapy, but radiation to the prostate also improves OS in low-volume disease. The recent high-quality RCTs, STAMPEDE and Hormonal Therapy Versus Hormonal Therapy Plus Local External Radiation Therapy in Patients With Primary Diagnosed Metastasized Prostate Cancer , concluded that adding radiation therapy to the prostate in mCSPC patients receiving ADT did not further improve their OS, the primary endpoint. In contrast, subgroup analyses by metastatic burden in the STAMPEDE trial showed OS benefit for patients with low-volume disease . The HORRAD trial also showed a similar trend without statistical significance in patients with < 5 metastatic lesions. Meta-analysis of 2 RCTs that involved 2493 patients suggested that ADT plus EBRT to the prostate was associated with improved OS as compared to ADT alone in men with low-volume metastatic burden however, this result was not observed in those with high-volume disease . Prostatectomy may also improve the oncologic outcomes in patients with oligometastatic prostate cancer. The definitive treatments, either radiation or prostatectomy, may be associated with survival benefit in patients with low metastatic burden. The results of several ongoing clinical trials on the benefit of prostatectomy and radiation to the prostate are expected to provide more information on this subject.
Genetic And Biochemical Biomarkers
A variety of markers have been studied for their ability to prognosticate patients and even predict response to treatment in the mCRPC setting. The most extensive data have come from analyses of circulating tumour cells. The rapidly evolving treatment landscape has meant that drugs commonly used in the castrate-resistant setting are now used in the mHSPC setting, and previously identified genetic aberrations in the mCRPC setting may have prognostic and/or predictive value earlier in the treatment paradigm. While this topic warrants a brief discussion, there is currently insufficient evidence in this field to suggest that genetic markers should guide treatment in the mHSPC setting.
Circulating tumour cells and AR splice variant 7 have been proposed as prognostic and predictive biomarkers in patients with mCRPC treated with enzalutamide and abiraterone acetate . Theoretically, the poor response in AR-V7-positive patients in the castrate-resistant setting may indicate that docetaxel will be more beneficial than androgen targeting in these patients. Results from small studies have suggested support for this hypothesis , although larger randomised trials and improved isolation and analysis of CTC will be required to validate these results.
Also Check: Bioidentical Hormone Replacement Therapy Orange County Ca
Drugs That Stop Androgens From Working
Anti-androgens
For most prostate cancer cells to grow, androgens have to attach to a protein in the prostate cancer cell called an androgen receptor. Anti-androgens are drugs that also connect to these receptors, keeping the androgens from causing tumor growth. Anti-androgens are also sometimes called androgen receptor antagonists.
Drugs of this type include:
They are taken daily as pills.
In the United States, anti-androgens are not often used by themselves:
- An anti-androgen may be added to treatment if orchiectomy or an LHRH agonist or antagonist is no longer working by itself.
- An anti-androgen is also sometimes given for a few weeks when an LHRH agonist is first started. This can help prevent a tumor flare.
- An anti-androgen can also be combined with orchiectomy or an LHRH agonist as first-line hormone therapy. This is called combined androgen blockade . There is still some debate as to whether CAB is more effective in this setting than using orchiectomy or an LHRH agonist alone. If there is a benefit, it appears to be small.
- In some men, if an anti-androgen is no longer working, simply stopping the anti-androgen can cause the cancer to stop growing for a short time. This is called the anti-androgen withdrawal effect, although it is not clear why it happens.
Newer anti-androgens
Enzalutamide , apalutamide and darolutamide are newer types of anti-androgens. They can sometimes be helpful even when older anti-androgens are not.
These drugs are taken as pills each day.
Risk Of Bias Assessment
Two investigators independently assessed risk of bias using predefined criteria. Disagreements were resolved by consensus. For randomized trials and cohort studies, methodologists adapted criteria for assessing risk of bias from the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. Criteria for randomized trials included use of appropriate randomization and allocation concealment methods, baseline comparability of groups, blinding, attrition, and use of intention-to-treat analysis. For cohort studies on prognostic factors, criteria included methods for assembling cohorts, attrition, blinding assessment of outcomes, and adjustment for potential confounding.
The methodology team assessed systematic reviews using AMSTAR 2 criteria. Criteria included use of pre-specified methods, appropriate search methods, assessment of risk of bias, and appropriate synthesis methods. Studies were rated as âlow risk of bias,ââmedium risk of bias,â or âhigh risk of biasâ based on the presence and seriousness of methodological shortcomings.
Studies rated âlow risk of biasâ are generally considered valid. âLow risk of biasâ randomized trials include clear descriptions of the population, setting, interventions, and comparison groups a valid method for allocation of patients to treatment low dropout rates and clear reporting of dropouts blinding of patients, care providers, and outcome assessors and appropriate analysis of outcomes.
Also Check: What Can Help Increase Estrogen Levels
Combined With Adt The Androgen
byMike Bassett, Staff Writer, MedPage Today September 7, 2022
In combination with androgen deprivation therapy , the novel androgen-receptor inhibitor rezvilutamide significantly improved radiographic progression-free survival and overall survival compared with bicalutamide in patients with high-volume, metastatic, hormone-sensitive prostate cancer, the phase III CHART trial showed.
Among 654 mostly Asian patients, median radiographic PFS was not reached in the rezvilutamide group compared with 25.1 months in the bicalutamide group at a median follow-up of 21.2 months, and overall survival was not reached in either group at a median follow-up of 29.3 months, reported Dingwei Ye, MD, of Fudan University Shanghai Cancer Center in China, and colleagues.
The 2-year radiographic PFS rate was 72.3% in the rezvilutamide group and 50.0% in the bicalutamide group, while the 2-year OS rates were 81.6% and 70.3%, respectively, they noted in Lancet Oncology.
The benefits of rezvilutamide on radiographic PFS were observed in all subgroups, except for patients with visceral metastases and those not from China.
“Rezvilutamide will be a welcome addition to the range of androgen-receptor inhibitors already available, and will — we hope — through a little healthy competition, overcome some of the barriers to real-world use of doublet therapy, such as cost and access,” Kostos and Murphy wrote.
Disclosures
The study was funded by Jiangsu Hengrui Pharmaceuticals.
Primary Source
Agents Without Survival Benefits
Although the evidence for the agents discussed so far is promising, additional agents have also been studied which have not shown benefit in prolonging OS. Bisphosphonates such as zoledronic acid have been examined based on the theory that reducing skeletal-related events may be of overall benefit in the course of metastatic prostate cancer. Sodium clodronate, a first-generation bisphosphonate, was examined in 2003 during the MRC PR05 trial. In this trial 311 men with metastatic prostate cancer who were on ADT were randomized to receive either oral sodium clodronate or placebo. At a median follow-up of 59 months, no statistical difference was detected in either bone PFS or OS with the addition of the drug.31 The STAMPEDE trial, as mentioned above, also added zoledronic acid as an additional experimental agent, comparing ADT alone to ADT plus zoledronic acid, as well as ADT plus docetaxel plus zoledronic acid to ADT plus docetaxel. In comparing the addition of zoledronic acid alone to ADT, there was no evidence of an OS advantage . In adding zoledronic acid to ADT plus docetaxel, both groups had an OS advantage compared to ADT alone but there was no evidence of an advantage of adding zoledronic acid to docetaxel .9
Recommended Reading: How Do You Check Your Testosterone Level
Treatment To Lower Testicular Androgen Levels
Androgen deprivation therapy, also called ADT, uses surgery or medicines to lower the levels of androgens made by the testicles.
Orchiectomy
Even though this is a type of surgery, its main effect is as a form of hormone therapy. In this operation, the surgeon removes the testicles, where most of the androgens are made. This causes most prostate cancers to stop growing or shrink for a time.
This is done as an outpatient procedure. It is probably the least expensive and simplest form of hormone therapy. But unlike some of the other treatments, it is permanent, and many men have trouble accepting the removal of their testicles. Because of this, they may choose treatment with drugs that lower hormone levels instead.
Some men having this surgery are concerned about how it will look afterward. If wanted, artificial testicles that look much like normal ones can be inserted into the scrotum.
LHRH agonists
Luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone agonists are drugs that lower the amount of testosterone made by the testicles. Treatment with these drugs is sometimes called medical castration because they lower androgen levels just as well as orchiectomy.
With these drugs, the testicles stay in place, but they will shrink over time, and they may even become too small to feel.
- Leuprolide mesylate
LHRH antagonists
Possible side effects
Many side effects of hormone therapy can be prevented or treated. For example:
In Five Years A Major Treatment Shift
In men diagnosed with metastatic hormone-sensitive prostate cancer, the cancer is typically driven to grow and spread by androgens that are produced largely in the testes. For many years, treatments that block androgen production have been a mainstay for men initially diagnosed with metastatic prostate cancer.
Starting in 2014, that began to change after a large clinical trial showed that adding the chemotherapy drug docetaxel to ADT improved how long men with hormone-responsive disease lived. Shortly after, another clinical trial showed that adding abiraterone to ADT also improved survival in these men, although primarily in men with many metastatic tumors, known as high-volume disease.
However, docetaxel, which works by directly killing cancer cells, can have substantial side effects, and some patients arent healthy enough to tolerate it. And abirateronewhich blocks androgen production throughout the bodycan also cause side effects, including those that affect the liver. It also has to be given in combination with the steroid prednisone, which carries its own toxicity.
Doing so, Dr. Chi said during a presentation of the TITAN data at the ASCO meeting, might help stave off the typically inevitable development of hormone-resistant cancer, which is more difficult to treat and a key driver of prostate cancer deaths.
Recommended Reading: Women’s Hormones At 50
Remission And The Chance Of Recurrence
A remission is when cancer cannot be detected in the body and there are no symptoms. This may also be called having no evidence of disease or NED.
A remission can be temporary or permanent. This uncertainty causes many people to worry that the cancer will come back. Although there are treatments to help prevent a recurrence, such as hormonal therapy and radiation therapy, it is important to talk with your doctor about the possibility of the cancer returning. There are tools your doctor can use, called nomograms, to estimate someone’s risk of recurrence. Understanding your risk of recurrence and the treatment options may help you feel more prepared if the cancer does return. Learn more about coping with the fear of recurrence.
In general, following surgery or radiation therapy, the PSA level in the blood usually drops. If the PSA level starts to rise again, it may be a sign that the cancer has come back. If the cancer returns after the original treatment, it is called recurrent cancer.
When this occurs, a new cycle of testing will begin again to learn as much as possible about the recurrence, including where the recurrence is located. The cancer may come back in the prostate , in the tissues or lymph nodes near the prostate , or in another part of the body, such as the bones, lungs, or liver . Sometimes the doctor cannot find a tumor even though the PSA level has increased. This is known as a PSA recurrence or biochemical recurrence.
When Is Hormone Therapy Used
Hormone therapy may be used:
- If the cancer has spread too far to be cured by surgery or radiation, or if you cant have these treatments for some other reason
- If the cancer remains or comes back after treatment with surgery or radiation therapy
- Along with radiation therapy as the initial treatment, if you are at higher risk of the cancer coming back after treatment
- Before radiation to try to shrink the cancer to make treatment more effective
You May Like: Does Low Estrogen Birth Control Cause Weight Gain
Patient Demographics And Clinical Characteristics
Patient demographics and clinical characteristics are presented in Table . Pairwise analyses revealed several significant differences between treatment groups , including for most recent PSA level, risk status and disease volume . Men treated with NHA or chemotherapy vs ADT alone had significantly higher PSA levels . Similarly, significantly higher proportions of patients receiving NHAs or chemotherapy vs ADT alone had high-risk status and high disease volume .
Table 3 Patient demographics and clinical characteristics
Searches And Article Selection
A research librarian conducted searches in Ovid MEDLINE , Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials , and Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews . An updated search was conducted prior to publication through January 20, 2020. The methodology team supplemented searches of electronic databases with the studies included in the prior AUA review and by reviewing reference lists of relevant articles.
The methodology team developed criteria for inclusion and exclusion of studies based on the Key Questions and the populations, interventions, comparators, outcomes, and settings of interest. The population was patients with advanced prostate cancer as described in Table 3. Treatments included first and second line antiandrogens, immunotherapy, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, surgery, radiopharmaceuticals, and surveillance strategies. Comparisons were against placebo, no therapy, or another active intervention and intermittent versus continuous therapy. Outcomes included overall survival , prostate cancer mortality, progression-free survival , prostate-specific antigen progression-free survival , failure-free survival, metastases-free survival, time to metastases, time to progression, skeletal events, and adverse events.
You May Like: Can Hormone Imbalance Cause Depression