Symptoms And Potential Complications
Imbalances in female hormones can have far-ranging effects on the body, producing a variety of physical, emotional and cognitive changes. These changes can cause symptoms that may include:
- Menstrual cycle changes, including shorter or longer times between periods, and periods that are longer, shorter, heavier or lighter than normal.
- Hot flashes and night sweats.
- Insomnia and other sleep disturbances
- Diminished sex drive
- Unexplained weight gain, especially in the abdominal area, hips and thighs
- Skin changes, such as thinning, dryness and wrinkling
- Dry, brittle hair
Female hormone imbalance can increase a womans risk of a number of diseases and health problems. Among the most serious of these is heart disease, with risk increasing as estrogen levels decrease. Women with hormonal imbalances are also at greater risk for osteoporosis, since low levels of estrogens can interfere with the absorption of calcium and other nutrients essential to the maintenance of bone health and density.
What Are Injectable Female Hormones Used For
Injectable female hormones are used in fertility treatment cycles to artificially control the menstrual cycle It allows for an optimization of the ovarian stimulation cycle in fertility treatment cycles, thereby increasing the chances of success.
If you would like more information about this, then please visit the following article: Ovarian induction.
What Is A Hormonal Imbalance
A hormonal imbalance occurs when your hormones are not produced at the proper levels. You can have many different types of hormonal imbalances. Sometimes, the imbalance means a deficiency in the given hormone while in other times, there might be an overflow. The kind of hormone that is imbalanced will play a major role in determining how the sign and symptoms will manifest and what would be the associated risks involved.
Though there are a few common life transitions that can cause a hormonal imbalance, such as menopause or pregnancy, you can struggle with such a problem at any point in your life. Both men and women can experience hormonal imbalances. Children, adolescents, adults, and the elderly may also find their hormones out of balance.
Because hormones and their functionalities are so varied, theres no one single way to detect a hormonal imbalance. A wide range of issues can indicate that something is amiss with your hormones. This is one of the reasons why your best bet is to get tested occasionally, especially when you start developing uncommon symptoms.
You May Like: Is The Birth Control Shot Hormonal
After Childbirth And Breastfeeding
Once pregnancy ends, hormone levels start to fall immediately. They eventually reach pre-pregnancy levels.
A sudden, significant drop in estrogen and progesterone may be a contributing factor in the development of postpartum depression.
Breastfeeding lowers estrogen levels and can prevent ovulation. This isnt always the case, however, so youll still need birth control to prevent another pregnancy.
What Is A Luteinizing Hormone Blood Test
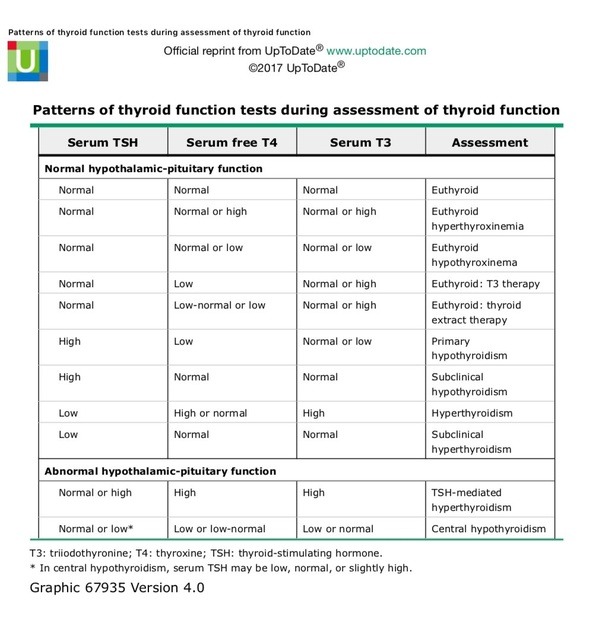
An LH blood test measures the amount of LH in your bloodstream. If youre a woman, the amount of this hormone in your bloodstream varies with age and throughout the menstrual cycle. It also changes with pregnancy. If a doctor orders a test for LH related to fertility, a woman may need multiple tests to track the rising and falling hormone levels. LH levels can also be measured by analyzing a urine sample.
If youre a man, your doctor can order an LH test to establish a baseline LH level. Your doctor can also measure your LH level after giving you an injection of gonadotropin releasing hormone . Measuring LH after receiving this hormone can tell your doctor if you have a problem with the pituitary gland or with another part of your body.
There are many reasons for your doctor to request an LH blood test. Levels of LH relate to menstrual issues, fertility, and the onset of puberty.
Examples of instances when a doctor may order an LH blood test include:
- a woman is having difficulty getting pregnant
- a woman has irregular or absent menstrual periods
- its suspected that a woman has entered menopause
- a man has signs of low testosterone levels, such as low muscle mass or decrease in sex drive
- a pituitary disorder is suspected
- a boy or girl appears to be entering puberty too late or too soon
Your doctor may order the LH blood test in coordination with other hormone measurements, such as testosterone, progesterone, FSH, and estradiol.
Also Check: Growth Hormone Deficiency Icd 10
Why Take A Womens Hormone Test
A hormone level test can tell you a lot about your bodyâs well-being. The test results can point you to a hormone imbalance, which can affect your health. This is because hormones regulate many vital functions in the body by acting as âchemical messengers.â So out-of-balance hormones can disrupt your bodyâs normal, healthy functioningâand result in a variety of symptoms.
For example, if your thyroid-stimulating hormones are out of balance, you might experience hormone imbalance symptoms like fatigue, cold sensitivity, irregular periods, dry skin, thinning hair, and more.
Or if your steroid hormones are imbalanced, you could have symptoms like increased body fat, lowered sex drive, loss of strength, and so on.
How Can I Balance Back My Hormones
If you have been diagnosed with a hormonal imbalance, your doctor can advise you on ways of bringing your body back into proper balance. Typical treatments for improved hormonal balance include hormone replacement therapy and lifestyle changes, such as dietary changes, stress management and exercise. In the case of thyroid dysfunction, medications and/or surgical intervention may be necessary to restore health levels of thyroid hormones.
You May Like: What Are Side Effects Of Hormone Replacement Therapy
What Are The Different Types Of Hormones
Endocrine glands are located throughout the body. These glands include the:
- Hypothalamus: controls thirst, hunger, sleep, sex drive, moods, body temperature, and the release of other hormones
- Parathyroid: controls calcium
- Thymus: controls the adaptive immune system
- Pancreas: controls blood sugar levels
- Thyroid: controls heart rate and calorie burn
- Adrenal: controls stress and sex drive
- Pituitary: controls growth
- Ovaries, in women: controls female sex hormones
- Testes, in men: controls male sex hormones
There are several different types of hormones in the body. When you have a hormonal imbalance, you may have a problem in one of more of these glands. The specific hormone thats imbalanced will determine the signs and symptoms that you experience as a result. Some of the major hormones found in the body include:
- Estrogen: controls sex drive in both men and women, and regulates the menstrual cycle in women
- Progesterone: influences the bodys changes through pregnancy
- Testosterone: controls sex drive in both men and women
- Cortisol: controls stress
- Melatonin: controls the bodys circadian rhythm and sleep cycles
- Serotonin: controls sleep cycles, appetite, and mood
- Growth hormone: controls the reproduction of cells and their subsequent growth
- Leptin: controls appetite, signaling when youre full
- Ghrelin: controls appetite, signaling when youre hungry
- Insulin: responds to sugar in the bloodstream
Commonly Asked Questions About Female Hormones
What is the lifelong role of estrogen in female health?
Most people think estrogen is primarily responsible for reproduction, but it also helps with bone, skin and cardiovascular health. In addition, it affects thyroid hormone production. During menopause, estrogen levels decline along with the production of progesterone and testosterone. Hormone replacement therapy , which means replacing lost hormones by re-introducing them into the body, is often suggested to offset the positive benefits of estrogen and can be helpful in reducing common symptoms of menopause. But some studies show that artificial doses of estrogen carry risks and have been linked to cancer, dementia, strokes and arthritis. Never assume that hormone replacement therapy is the right thing to do without consulting your healthcare provider.
What is Puberty? Hormones that control puberty
Puberty is the time in life when children begin to show changes through hormone secretions that indicate they are about to become adults physically. In girls, the most obvious sign of puberty is the onset of menstruation. It can happen anywhere between the ages of 9 17, with a median age of 12. The menses, or monthly cycle, is interrupted during pregnancy and typically ends when the ovaries stop secreting steroid hormones a stage known as menopause.
What are the hormonal milestones in a females life?
What Causes Hot Flashes?
Why do I feel so different during my monthly cycle?
Why dont men have monthly cycles?
Also Check: How To Beat Hormonal Acne
Use Your Symptoms As Your Guide
For more serious cases and symptoms, hormone testing can be very helpful. But for most women who experience the normal, if unpleasant, fluctuations of hormones during perimenopause and menopause, hormone tests are not generally needed nor will they offer many answers. The best way to measure your hormones during perimenopause and menopause is to evaluate your symptoms. Take our quick hormonal profile to see how your symptoms rate.
What Is Hormonal Imbalance In Men
The most common hormonal imbalances in men are related to testosterone levels. Men may experience low levels of testosterone due to disorders, like hypogonadism for example when the testes cannot produce an adequate supply of testosterone. More commonly, aging is the underlying cause, with testosterone production gradually diminishing over time, beginning around age 40. For some men, levels fall so low that the bodys basic needs for the hormone cannot be fulfilled, which can lead to many of the symptoms listed above. Other factors that can contribute to low testosterone levels include excessive stress, poor diet, obesity and regular excessive alcohol use.
Also Check: How Can You Tell If Your Hormone Levels Are Off
How Is Low Testosterone Diagnosed What Treatments Are Available
Most healthcare providers will measure their testosterone levels by having a blood test, doing a physical exam and having the patient describe his symptoms. Finally, they may order additional tests to rule out other possible diagnoses.
Testosterone is sometimes prescribed for men with low testosterone. Almost all hormone supplements and testosterone treatments are available in different forms, including lozenges, patches, gels and creams.
Because of the limited knowledge regarding this condition, challenges in having a proper diagnosis, as well as the possible side effects of treatments, HRT should not administer for men without proper testing, retesting and consultation with a healthcare provider to discuss the pros and cons. One may want to consider an endocrinologist who specializes in hormones.
Your Comprehensive Female Hormone Test List
Most female sex hormones are steroid hormones, meaning that theyre made of lipids . Theyre produced and secreted by many different glands in the body, including the pituitary gland, adrenal glands, thyroid gland, and ovaries .
Some of the most commonly measured female hormones and hormonal markers include :
- Estrone, estradiol, and estriol : A female sex hormone that regulates sex characteristics and maintains reproductive, bone, and cardiovascular health in women.
- Progesterone: A female sex hormones that regulates the menstrual cycle and thickens the uterine lining to prepare for follicle implantation in women.
- Total testosterone and free testosterone: An androgen that plays an important role in female reproductive health and libido.
- Luteinizing hormone : A pituitary hormone that regulates the production of other sex hormones, like progesterone and estrogen, and induces ovulation in women.
- Follicle-stimulating hormone : A pituitary hormone that causes estrogen levels to rise in women and leads to the development of follicles in the ovaries.
- Dehydroepiandrosterone and DHEA-sulfate: An androgen produced by the adrenal glands thats a precursor to other sex hormones and helps produce testosterone in women.
- Sex hormone-binding globulin : A protein that helps bind up excess sex hormones, like testosterone and estrogen.
- Prolactin: A hormone produced in the pituitary that promotes breast milk production, but can suppress fertility when elevated.
- Thyroid-stimulating hormone
You May Like: Hormonal Imbalance Acne On Chin
At What Age Should Amh Be Examined
Anti-Müllerian hormone is produced by the ovary, and its blood levels are an indicator of a woman’s ovarian reserve.
To ensure everything works as expected, we recommend that the first measurement is done from age 20 and not later than age 30. By doing this, if a woman has a diminished ovarian reserve at a young age, she would have time to decide whether she wants to have a baby now or cryopreserve some eggs to become a mother in the future.
What Is A Good Amh Level For Your Age
AMH levels naturally decline with age, so its normal to see a lower ovarian reserve in your 30s, 40s and 50s.
For actual numbers, consider these estimates, which are on the lower side of the spectrum for each respective age:
- 25 years old: 3.0 ng/mL.
- 30 years old: 2.5 ng/mL.
- 35 years old: 1.5 ng/ mL.
- 40 years old: 1 ng/mL.
- 45 years old: 0.5 ng/mL.
Higher AMH levels arent always a good thing. AMH may be high in some people with polycystic ovary syndrome .
You May Like: How To Treat Hormonal Acne In Your 30’s
Hormone Level Testing Can Help
So how do you know if youre experiencing abnormally low levels of female hormones? A blood test for hormone levels can help you determine if youre experiencing low than usual levels of female hormones as you age.
Hormone level blood testing can help :
- Identify low levels of female hormones in your system
- Determine if low female hormone levels are causing your pre-existing health problems
- Determine if youre a good candidate for hormone replacement therapy as a perimenopausal or menopausal woman
A simple clinical blood test can help measure all of the above and determine if lower hormone levels are causing your changes in overall wellness.
How Menopause Affects Hormone Levels
As women begin to enter their 40s, they may start to go through menopause. Menopause marks the beginning of the female body winding down from being able to bear children to be beyond the age of childbearing. In essence, monthly periods cease.
This process can take several years, and once menopause is over, your body will no longer be able to bear children. The process involves three stages:
- Perimenopause. This stage describes the years leading up to the cessation of monthly periods. The ovaries will begin to produce less estrogen in this stage. It can last as long as ten years and often involves irregular periods, weight gain, and hormonal imbalance.
- Menopause. Menopause is when a womans ovaries have wholly stopped releasing eggs, and she can no longer become pregnant. Hormonal changes are widespread in this stage, too.
- Postmenopause. This is the period in a womans life when she has gone more than 12 months without a period. Hormonal changes have abated mainly at this stage, which will last for the rest of the womans life.
This process can look different for many women but includes changes in the menstrual cycle and hormone levels and often includes hot flashes, trouble sleeping, and mood swings.
You May Like: Hormones And Weight Gain After 40
Timing For Female Hormone Testing
Throughout our life, male or female, many of us reach a point where things may not feel quite right. Our energy levels may be low our desire for sexual activity is not what it used to be if it exists at all. We may be experiencing unexplained weight gain or muscle loss, not to mention issues with fertility. It is for these reasons many men and women will seek out treatment options. Such options sought out by both sexes have increasingly been hormone treatment plans, which almost always begin with blood testing. This process is relatively more straightforward for most men, but female hormone testing is slightly more complicated. Timing for the female hormone blood panels is an essential factor that must be taken into consideration.
How To Test Cortisol Levels
Cortisol levels are measured with lab tests. These may be blood tests, which measure levels of the hormone in the bloodstream, or saliva tests, which measure cortisol levels in a saliva sample. Cortisol testing is typically done early in the morning, when levels are normally highest. Often, to produce the most accurate results, testing is repeated in the afternoon of the same day. Cortisol testing is often done in conjunction with ACTH level tests, since this pituitary gland hormone works to regulate cortisone levels. ACTH tests measure levels of the hormone in the bloodstream.
Getting tested can be done through your health care provider, who can order your tests for you, take your blood or saliva samples or send you to a lab to have them done. Then, your provider will let you know your results once they are delivered to his or her office.
You can also order these lab tests yourself online or over the phone from independent testing services, like Health Testing Centers. Ordering your own tests is generally less expensive, since you skip the cost of an office visit, and more efficient, since the results are delivered directly to you.
However, it is important to note that if your tests show that your cortisol and/or ACTH levels are abnormal too high or too low following up on those results with a visit to your healthcare provider is essential. Abnormal levels of these important hormones require further examination and testing.
Recommended Reading: Does 7 11 Sell Melatonin
What Are Blood Tests Used For
Blood tests are common medical tests used by healthcare providers to diagnose medical conditions, assess overall health, monitor chronic conditions, or see how well a medication or treatment is working.
Normal ranges for blood test results may include:
- Different liver enzymes are tested to determine cellular dysfunction versus cellular damage versus liver obstruction
- ALT Female 7-30 units/L Male 10-55 units/L
- Alkaline phosphatase Female 30-100 units/L Male 45-115 units/L
- AST Female 9-25 units/L Male 10-40 units/L
- Bilirubin total 0.0-1.0 mg/dL
- Gamma glutamyl transferase Female 45 U/L Male 65 U/L
- Lactate dehydrogenase 270 U/L