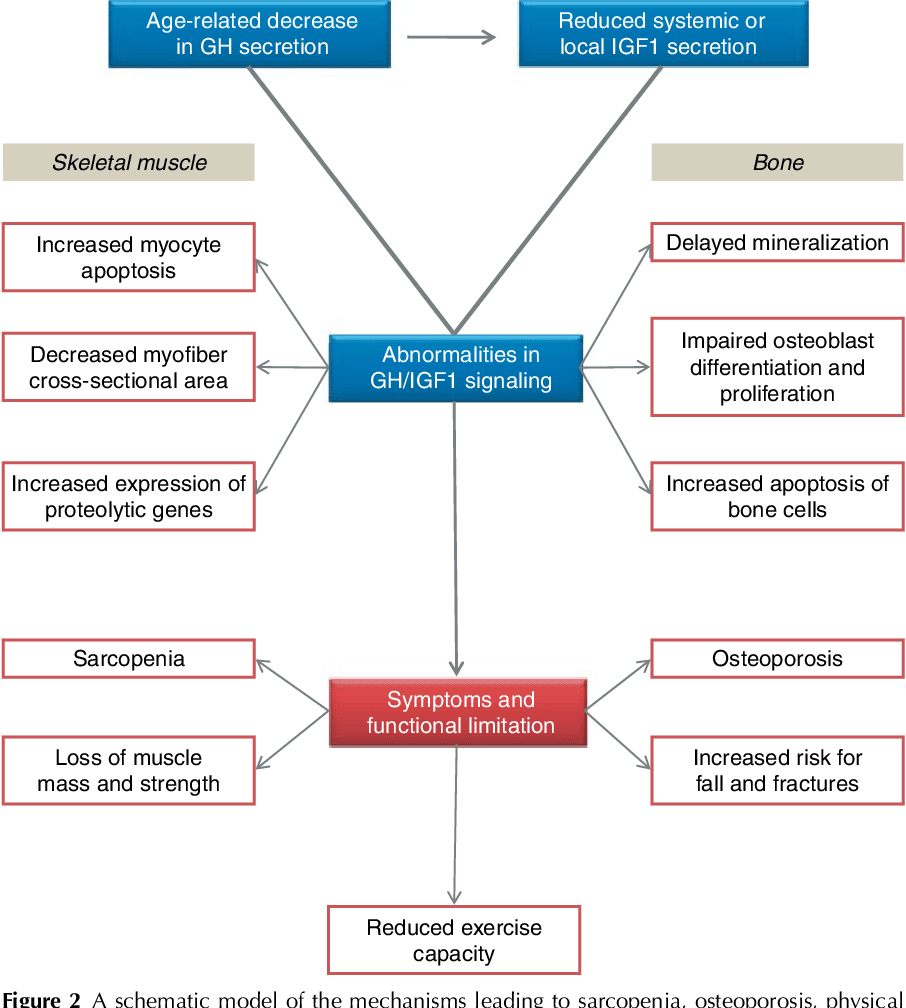
Macimorelin Oral Stimulation Test
Macimorelin is available as an oral solution of 60 mg white to off-white granules in a pouch for reconstitution in 120 mL of water, resulting in a solution of 0.5 mg/mL of macimorelin.
Dosing and Administration Recommendations
- Recommended dose is 0.5 mg/kg as a single oral dose, after fasting for at least 8 hours.
- Discontinue therapy with strong CYP3A4 inducers, growth hormones and drugs that affect GH release for an adequate length of time before administering macimorelin.
- Adequately replace other hormone deficiencies before administering macimorelin.
Note: Serum GH level of less than 2.8 ng/mL following macimorelin administration confirms the presence of adult growth hormone deficiency.
Hypofunction And Other Disorders Of The Pituitary Gland
- 20162017201820192020202120222023Non-Billable/Non-Specific Code
- short stature due to endocrine disorder
- Anterior pituitary hormone deficiency
- Female infertility due to pituitary disorder
- Female infertility of pituitary origin
- Follicle stimulating hormone deficiency
- Fsh – follicle stimulating hormone deficiency
- Gonadotropin deficiency, isolated
- Growth hormone deficiency after bone marrow transplant
- Growth hormone deficiency, bone marrow transplant
- Growth hormone deficiency, isolated
- Somatotropin deficiency, partial
- 643 Endocrine disorders with mcc
- 644 Endocrine disorders with cc
- 645 Endocrine disorders without cc/mcc
Disorders Of Other Endocrine Glandstype 1 Excludes
- 20162017201820192020202120222023Non-Billable/Non-Specific Code
Type 1 Excludes
- Arthropathy assoc w endocrine disorder
- Arthropathy due to endocrine disorder
- Arthropathy with endocrine disorder
- Hypertension secondary to endocrine disorder
- Low testosterone
- Secondary hypertension due to endocrine disorders
- Any deviation from the normal structure or function of the endocrine system that is manifested by a characteristic set of symptoms and signs.
- Impairment of health or a condition of abnormal functioning of the system of glands that release their secretions directly into the circulatory system.
- Pathological processes of the endocrine glands, and diseases resulting from abnormal level of available hormones.
- Your endocrine system includes eight major glands throughout your body. These glands make hormones. Hormones are chemical messengers. They travel through your bloodstream to tissues or organs. Hormones work slowly and affect body processes from head to toe. These include
- growth and development
- metabolism – digestion, elimination, breathing, blood circulation and maintaining body temperature
- sexual function
- 643 Endocrine disorders with mcc
- 644 Endocrine disorders with cc
- 645 Endocrine disorders without cc/mcc
You May Like: Does Melatonin Put You To Sleep
Other Congenital Malformation Syndromes Predominantly Associated With Short Stature
- 2020 – New Code202120222023Billable/Specific CodePOA Exempt
- 20162017201820192020202120222023Billable/Specific Code
Applicable To
- 20162017201820192020202120222023Billable/Specific Code
Applicable To
- Applicable To annotations, or
Retarded Development Following Protein
- 20162017201820192020202120222023Billable/Specific Code
- 20162017201820192020202120222023Billable/Specific Code
Applicable To
- 20162017201820192020202120222023Billable/Specific Code
Applicable To
- 20162017201820192020202120222023Billable/Specific Code
Applicable To
Read Also: Are Spermicidal Methods Of Contraception More Effective Than Hormonal Methods
Symptoms Of Growth Hormone Deficiency
Children with GHD are shorter than their peers and have younger-looking, rounder faces. They may also have baby fat around the abdomen, even though their body proportions are average.
If GHD develops later in a childs life, such as from a brain injury or tumor, its main symptom is delayed puberty. In some instances, sexual development is halted.
Many teens with GHD experience low self-esteem due to developmental delays, such as short stature or a slow rate of maturing. For example, young women may not develop breasts and young mens voices may not change at the same rate as their peers.
Reduced bone strength is another symptom of AGHD. This may lead to more frequent fractures, especially in older adults.
People with low growth hormone levels may feel tired and lack stamina. They may experience sensitivity to hot or cold temperatures.
Those with GHD may experience certain psychological effects, including:
- bouts of anxiety or emotional distress
Adults with AGHD typically have high levels of fat in the blood and high cholesterol. This isnt due to poor diet, but rather to changes in the bodys metabolism caused by low levels of growth hormone. Adults with AGHD are at greater risk for diabetes and heart disease.
Diagnosis Of Growth Hormone Deficiency
Pediatric endocrinologists are the physicians who specialize in diagnosis and treatment of growth hormone deficiency and growth problems in children. Internist endocrinologists are the physicians with the most expertise in assessment and treatment of adult GH deficiency.
Although GH can be readily measured in a blood sample, testing for GH deficiency is constrained by the fact that levels are nearly undetectable for most of the day. This makes simple measurement of GH in a single blood sample useless for detecting deficiency. Physicians therefore use a combination of indirect and direct criteria.
Several types of evidence are used to ascertain GH sufficiency or deficiency.
- Auxologic criteria
- Indirect hormonal criteria
- Direct hormonal criteria
- Response to GH treatment
- Corroborative evidence of pituitary dysfunction
“Provocative tests” involve giving a dose of an agent that will normally provoke a pituitary to release a burst of growth hormone. An intravenous line is established, the agent is given, and small amounts of blood are drawn at 15 minute intervals over the next hour to determine if a rise of GH was provoked. Agents which have been used clinically to stimulate and assess GH secretion are arginine, levodopa, clonidine, epinephrine and propranolol, glucagon and insulin.
Severe GH deficiency in childhood has the following measurable characteristics:
- Proportional stature well below that expected for family heights
- Below-normal velocity of growth
You May Like: Does Melatonin Come In Liquid Form
How Is Growth Hormone Deficiency Diagnosed
Your childs doctor will look for signs of GHD if your child isnt meeting their height and weight milestones. Theyll ask you about your growth rate as you approached puberty, as well as your other childrens growth rates. If they suspect GHD, a number of tests can confirm the diagnosis.
Your levels of growth hormone fluctuate widely throughout the day and night . A blood test with a lower-than-normal result isnt enough evidence in itself to make a diagnosis.
One blood test can measure levels of proteins which are markers of growth hormone function but are much more stable. These are IGF-1 and IGFPB-3 .
Your doctor may then go on to a GH stimulation test, if screening tests suggest that you have a GH deficiency.
Growth plates are the developing tissue at each end of your arm and leg bones. Growth plates fuse together when youve finished developing. X-rays of your childs hand can indicate their level of bone growth.
If a childs bone age is younger than their chronological age, this might be due to GHD.
If your doctor suspects a tumor or other damage to the pituitary gland, an MRI imaging scan can provide a detailed look inside the brain. Growth hormone levels will often be screened in adults who have a history of pituitary disorders, a brain injury, or who need brain surgery.
Testing can determine whether the pituitary condition was present at birth or brought on by an injury or tumor.
How Is Growth Hormone Deficiency Treated
Since the mid-1980s, synthetic growth hormones have been used with great success to treat children and adults. Before synthetic growth hormones, natural growth hormones from cadavers were used for treatment.
Growth hormone is given by injection, typically into the bodys fatty tissues, such as the back of the arms, thighs, or buttocks. Its most effective as a daily treatment.
Side effects are generally minor, but may include:
- redness at the injection site
- curving of the spine
In rare cases, long-term growth hormone injections may contribute to the development of diabetes, especially in people with a family history of that disease.
Don’t Miss: Upper Body Weight Gain Hormones
Treatment Of Gh Deficiency In Childhood
When treated with GH, a severely deficient child will begin to grow faster within months. In the first year of treatment, the rate of growth may increase from half as fast as other children are growing to twice as fast . Growth typically slows in subsequent years, but usually remains above normal so that over several years a child who had fallen far behind in his height may grow into the normal height range. Parents often notice increased strength, appetite, and energy. Increased muscle strength may allow young children to overcome delays of motor development. Excess adipose tissue may be reduced.
There are almost no significant side effects of this type of physiologic replacement. Rare risks and unsettled issues are discussed in the article on GH treatment, but GH deficient children receiving replacement doses are at the lowest risk for problems and receive the greatest benefit.
Little except the cost of treating severely deficient children is controversial, and it is likely that the majority of children with severe growth hormone deficiency in North America, Japan, and much of Europe and the rest of the developed world are offered treatment, and most accept. The story is very different for adult deficiency.
- For more details on treatment of Growth Hormone Deficiency, see Growth hormone treatment.
What Causes Growth Hormone Deficiency
GHD that isnt present at birth may be caused by a tumor in the brain. These tumors are normally located at the site of the pituitary gland or the nearby hypothalamus region of the brain.
In children and adults, serious head injuries, infections, and radiation treatments can also cause GHD. This is called acquired growth hormone deficiency .
Most cases of GHD are idiopathic, meaning that no cause has yet been found.
Also Check: What Is Thyroid Hormone Replacement
Study Design And Setting
Patients with International Classification of Diseases diagnoses of hypopituitarism, or other diagnoses of pituitary disorders assumed to be associated with an increased risk of hypopituitarism, recorded in the DNPR during 20002012 were identified. Medical records were reviewed to confirm or disprove hypopituitarism.
Appendix C: Requirements For Gh
Testing for adult GHD is not required
- Three or more pituitary hormone deficiencies and low IGF-1
- Congenital structural abnormalities
- Transcription factor defects (PIT-1, PROP-1, LHX3/4, HESX-1, PITX-2
- GHRH receptor-gene defects
- GH-gene defects associated with brain structural defects
- Single central incisor
Acquired causes such as perinatal insults
Testing for adult GHD is required
- Neoplastic sellar and parasellar lesions
- Autoimmune hypophsitis
Read Also: How To Find Out If You Have Low Testosterone
Appendix A: Examples Of Hypothalamic/pituitary/cns Disorders
Congenital genetic abnormalities
- Transcription factor defects
- Growth hormone releasing hormone receptor gene defects
- GH secretagogue receptor gene defects
- GH gene defects
- Other mid-line defects
- Vascular malformations
Acquired structural abnormalities
- CNS tumors/neoplasms
- Inflammatory processes
- Infiltrative processes
- Head trauma/traumatic brain injury
- Surgery of the pituitary or hypothalamus
Gh Stimulation In Children
The exercise stimulation test is often used as an initial screen for GH deficiency, but combinations of other tests have been advocated by various institutions. A subnormal response from a single provocative test is not diagnostic for GH deficiency and should be confirmed with a second provocative test. These tests produce an increase in plasma GH to > 7 ng/mL in individuals with appropriate GH production.1-3 Some institutions use 10 ng/mL as a cutoff for normal GH response.1,3
The insulin-induced hypoglycemia and the GHRH tests provide additional information beyond establishing GH deficiency. The insulin-induced hypoglycemia test allows the assessment of the entire hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis. A normal GH response to GHRH in a patient proven to be GH deficient by previous stimulation testing suggests that the GH deficiency is due to insufficient GHRH production by the hypothalamus.
Due to low baseline levels of GH, prepubertal children should be primed prior to performing the stimulation tests by one of the following:3
You May Like: Foods For Women’s Hormones
Short Stature Due To Endocrine Disorder
- 20162017201820192020202120222023 – Converted to Parent CodeNon-Billable/Non-Specific Code
- E34.3 should not be used for reimbursement purposes as there are multiple codes below it that contain a greater level of detail.
- ICD-10-CM E34.3 is a new 2023 ICD-10-CM code that became effective on October 1, 2022.
- This is the American ICD-10-CM version of E34.3 – other international versions of ICD-10 E34.3 may differ.
type 1 excludes
- achondroplastic short stature (
- 20162017201820192020202120222023Billable/Specific CodePOA Exempt
Applicable To
- 20162017201820192020202120222023Billable/Specific CodePOA Exempt
Applicable To
Other Cpt Codes Related To The Cpb:
70450 – 70470 Computed tomography, head or brain without contrast material, with contrast material, or without contrast material, followed by contrast material and further sections 70496 Computed tomography angiography, head, with contrast material, including noncontrast images, if performed, and image postprocessing 70551 – 70553 Magnetic resonance imaging, brain without contrast material, with contrast material, or without contrast material, followed by contrast material and further sequences 70554 – 70555 Magnetic resonance imaging, brain, functional MRI 80418 Combined rapid anterior pituitary evaluation panel 80422 Glucagon tolerance panel for insulinoma 80428 – 80430 Growth hormone stimulation panel or growth hormone suppression panel 80434 Insulin tolerance panel for ACTH insufficiency 80435 Growth hormone, human 84305 Growth hormone, human , antibody 88271 – 88275 Cytogenetics and molecular cytogenetics, interpretation and report 96372 Therapeutic, prophylactic or diagnostic injection subcutaneous or intramuscular 99601 – 99602
Also Check: Does Medicaid Cover Hormone Replacement Therapy In Nc
Gh Stimulation In Adults
The insulin-induced hypoglycemia test is considered to be the test of choice for diagnosing GH deficiency in adults.4 Since this test involves some risk to the patient , the GHRH + arginine test has been proposed as an equally sensitive alternative.5 Most normal adults will produce a GH concentration > 5 ng/mL after either of these stimulation protocols. Severe GH deficiency has been defined as the inability to produce GH levels > 3 ng/mL during these tests.4,5
Gh Therapy In Children
Growth hormone deficiency involves abnormally short stature with normal body proportions. Growth hormone deficiency can be categorized as either congenital or acquired. An abnormally short height in childhood may occur if the pituitary gland does not produce enough growth hormone. It can be caused by a variety of genetic mutations , absence of the pituitary gland, or severe brain injury, but in most cases no underlying cause of the deficiency is found.
The FDA has approved GH for use in the following pediatric conditions: GHD, Turner syndrome, chronic renal insufficiency before transplantation, and children born small for gestational age. An advisory committee to the FDA also recommended approval of GH for children with idiopathic short stature.
An assessment conducted for the National Institute of Clinical Excellence suggests the following criteria be used to define subnormal growth in children with GHD:
In addition, retardation of bone maturation is found in most cases of subnormal growth.
Read Also: What Supplements Should I Take For Hormonal Imbalance
Short Stature Due To Endocrine Disordere343
Chapter 4 – Endocrine, nutritional and metabolic diseases » Disorders of other endocrine glands » Short stature due to endocrine disorder
Related MeSH Terms
Diseases » Endocrine System Diseases » Dwarfism
A genetic or pathological condition that is characterized by short stature and undersize. Abnormal skeletal growth usually results in an adult who is significantly below the average height. MeSH
Diseases » Endocrine System Diseases » Dwarfism » Laron Syndrome
An autosomal recessive disorder characterized by short stature, defective GROWTH HORMONE RECEPTOR, and failure to generate INSULIN-LIKE GROWTH FACTOR I by GROWTH HORMONE. Laron syndrome is not a form of primary pituitary dwarfism but the result of mutation of the human GHR gene on chromosome 5. MeSH
Hierarchy Tree View
YOU AGREE THAT THE INFORMATION PROVIDED ON THIS WEBSITE IS PROVIDED AS IS, WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR ANY PARTICULAR PURPOSE, OR NON-INFRINGEMENT OF ANY THIRD-PARTY PATENT, COPYRIGHT, OR ANY OTHER THIRD-PARTY RIGHT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE CREATORS OF THE WEBSITE OR WASHINGTON UNIVERSITY BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, SPECIAL, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES ARISING OUT OF OR IN ANY WAY CONNECTED WITH THE WEBSITE, THE USE OF THE WEBSITE, OR THIS AGREEMENT, WHETHER IN BREACH OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, EVEN IF SUCH PARTY IS ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES.
Pancreas / Insulin Glucagon
Other disorders of glucose regulation and pancreatic internal secretion
- Nondiabetic hypoglycaemic coma
- Drug-induced insulin coma in nondiabetic
- Hyperinsulinism with hypoglycaemic coma
- Hyperplasia of pancreatic islet beta cells NOS
- Posthypoglycaemic coma encephalopathy
You May Like: How Can You Treat Hormonal Acne
What Is Growth Hormone Deficiency
A growth hormone deficiency occurs when the pituitary gland doesnt produce enough growth hormone. It affects children more often than adults.
The pituitary gland is a small gland about the size of a pea. Its located at the base of the skull and secretes eight hormones. Some of these hormones control thyroid activity and body temperature.
GHD occurs in roughly 1 out of 7,000 births. The condition is also a symptom of several genetic diseases, including Prader-Willi syndrome.
You may be concerned that your child isnt meeting height and weight growth standards. But if its GHD, its important to know that its treatable. Children who are diagnosed early often recover very well. If left untreated, the condition can result in shorter-than-average height and delayed puberty.
Your body still needs growth hormone after youve finished puberty. Once youre in adulthood, the growth hormone maintains your body structure and metabolism. Adults can also develop GHD, but it isnt as common.